Translate this page into:
Pain and Wound Management in Fungating Merkel Cell Carcinoma within a Palliative Setting: The First Case Report of this Predicament
*Corresponding author: Shaan Mohan, School of Medicine, College of Life Sciences, Leicester Medical School, Leicester, United Kingdom. mrshaanmohan@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Mohan S, Khan A. Pain and Wound Management in Fungating Merkel Cell Carcinoma within a Palliative Setting: The First Case Report of this Predicament. Indian J Palliat Care. 2024;30:81-4. doi: 10.25259/IJPC_259_2023
Abstract
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare type of skin cancer of the neuroendocrine Merkel mechanoreceptors. These cells are closely associated with nerve terminals and, given their proximity to cutaneous tissue, have the propensity to develop into deeply ulcerated, fungating malignancies. These friable wounds are easily irritated, and can cause significant pain for patients. We report a palliative case of severe, fungating MCC of the left scalp where the main contributor to the patient’s illness burden is pain. Having been referred to palliative care by the Tissue Viability team, this 90-year-old gentleman was complaining of episodic burning pain during dressing changes, which was associated with radiation to the forehead, nausea, and significant trait anxiety. It was theorised that this pain could be in part due to tension headache, not just nociception, and anticipatory lorazepam was prescribed to relieve trait anxiety. All symptoms were majorly relieved following this administration. A specialist dressing was implemented to absorb exudate and balance moisture, which we believe may have stopped further deterioration of pain. Overall, this report emphasises the need to consider alternative pain aetiologies other than nociception in a presentation that is not found in the literature.
Keywords
Fungating
Merkel
Carcinoma
Palliative
Pain
INTRODUCTION
The epithet ‘fungating’ is a misnomer as it does not refer to fungal infection; instead, it denotes when the skin and its nutrient vasculature are infiltrated by a primary or secondary tumour, a phenomenon that is often seen in palliative care and which lacks evidence and protocols for its management. In mycology, fungi adopt certain ‘peculiar methods of hyphal growth’ amidst their pursuit to conquer new forest territory,[1] and it is these protuberant hyphae that inspire the word ‘fungating.’ By virtue of the vascular infiltration within a fungating lesion, these wounds are easily friable and, therefore, provide a challenge in symptomatic relief.[2] From a patient’s perspective, pain management can be one of the most predominant challenges of fungating wounds, as demonstrated in this report.
Merkel cells are neuroendocrine mechanoreceptors in the skin that help detect touch, and perhaps their close association with nerve terminals increases their capacity to elicit pain;[3] it is therefore surprising that fungating Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) in a palliative setting has not been reported in the literature, given that MCC can cause dire straits of pain for patients as we shall illustrate. MCC is 40 times rarer than melanoma;[4] thus, it is important to document the complete natural history of this disease, which may well involve palliative care. Given that skin cancers typically present in sun-exposed areas like the head and neck, pain management can be intrusive and distressing for patients. This is especially true for fungating lesions. Having identified a gulf in the literature, we seek to bridge this, starting with this case report, for which we use the 2013 CARE Checklist where possible.
CASE REPORT
A 90-year-old gentleman was referred to hospice care by the community Tissue Viability team within an English Healthcare Trust. The Tissue Viability team is responsible for managing complex, non-healing wounds, including those that are fungating.[5] The gentleman’s lesion is depicted in Figure 1 and demonstrates a fungating, ulcerated lesion predominantly of the left scalp with nuchal extension. Having significant past sun overexposure without protection, this gentleman had a vast history of 17 skin cancers, some of which had warranted plastic surgery such as ear reconstruction and nasal flaps. Following a diagnosis of MCC by Tru-Cut biopsy two years prior, the patient was given two options: Surgery with curative intent or palliative radiotherapy. Initially, surgery was elected, after which the patient received wide local excision and skull flap reconstruction. Histology revealed 35 mm MCC with a deep margin of 1 mm and a peripheral margin clear by over 5 mm, with evidence of lymphovascular invasion. In the present relapse of this disease, the patient is under palliative care.

- Fungating lesion.
The main symptom this gentleman had vis-a-vis his scalp lesion, now within a palliative setting, was ‘indescribable’ pain. This pain was particularly noticeable when the wound dressing was changed, a daily event that caused him severe trait anxiety. The episodic pain was depicted by him as nauseating, burning, and with radiation to the forehead; the oxycodone he was taking did not alleviate these symptoms whatsoever (and this oxycodone was reverted back to morphine following improvement in his renal function). This clinical picture had elements of nociceptive pain but also tension headache with the pathognomonic forehead radiation and associated anxiety.[6] In addition, the patient also complained of leaking exudate from the wound dressing, which disrupted his daily activities and may have contributed to the pain.
Given the severe trait anxiety and tension-sounding headache, it was decided to prescribe anticipatory lorazepam; this was administered orally 30 min before wound dressing changes. Two days after the advent of this prescription, the patient reported less anxiety, absence of pain radiation to the forehead, and nausea relief.
Regarding the patient’s exudative leakage, the following wound dressing regime was masterminded by a specialist palliative care nurse. Table 1 summarises the methods with the intended purpose.
| Method | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Octenidine wound irrigation | Antisepsis of Gram-positive and Gram-negative, especially Pseudomonas species |
| Aquacel wound dressing (silver impregnated) | Absorbs exudate and balances moisture |
| Kerramax dressing | Specifically designed to be super-absorbent of exudate |
| Beige tubular bandage | To fix wound dressings and create a 'cap.' |
| Clear film | To seal in exudates that have been absorbed by deeper dressings, preventing leakage. |
| Flaminel forte cream | Balances moisture |
Following the implementation of this wound dressing regime, which is depicted in Figure 2, the patient reported minimal exudative leakage. It is thought that the decreased exudate stagnation may have also contributed to the pain relief in this gentleman.[7]
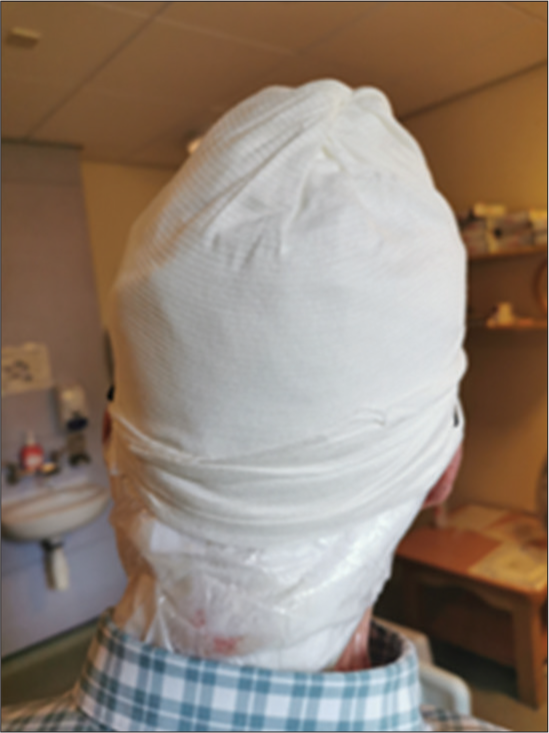
- Specialist wound dressing.
Statement of holistic care
It would be prudent to mention this gentleman’s other concerns, including how his social, psychological, and spiritual well-being was looked after at this hospice. From a broad, non-specific perspective, this hospice was adapted to provide personable care: It had its hairdresser, rooms that opened onto patios, well-being rooms, a multi-faith centre, and were often frequented by a cat (which many patients reported as therapeutic). Notwithstanding such amenities, it was important to examine this gentleman’s well-being. His appearance was unwaveringly well-kempt, and he did not exhibit any stigmata of disease when his dressing was on; his engagement and rapport in our interchanges were positive and undistracted, although sometimes affected by hearing deficit. His tone, volume, and fluency of speech were good and noticeably improved following improvements in the quality of his care. It is vital to note that this gentleman’s perception was affected by nocturnal pseudo-hallucinations, but these disappeared after stopping the oxycodone. The patient described how being in the hospice eased the burden off his shoulders in terms of wound care, and he described the staff as ‘very reassuring and well-prepared.’ He was accompanied by a relative at most times, who provided turf for social interaction and indubitably improved this gentleman’s psychological well-being. While no metric for patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) was utilised per se, we would subjectively assess this patient’s well-being to have been on a positive trajectory, although we are aware that this migratory wound might pose a significant challenge in this patient’s future care.
DISCUSSION
A search of PubMed-indexed literature reveals the earliest use of the term ‘fungating’ to be Pitt et al.’s 1904 case series[8] on fungating endocarditis, in which valvular vegetations are described. Since then, fungating wounds have been increasingly recognised within palliative care literature, as they are often manifestations of late-stage metastatic disease, which has become infamous for its non-healing properties.[2] The purpose of this case report was to present the unique challenge of managing a fungating wound that is in a particularly challenging location, the scalp, which interferes with daily activities like sitting back in an armchair and lying down to sleep. Moreover, this case is the first documented case of fungating MCC in palliative care, whereby ‘fungating’ AND ‘Merkel cell carcinoma’ AND (‘palliative’ OR ‘hospice’) yields zero search results in PubMed, demonstrating that further evidence is needed within the natural history of MCC. When (‘palliative’ OR ‘hospice’) is excluded from search terms, four results are yielded, two of which were impertinent to fungating MCC. We systematically reviewed the remaining two articles. Article 1 by Hu et al.[9] reports the novel use of crushed metronidazole tablets in treating malodour in fungating MCC, which demonstrated an immediate therapeutic effect. Article 2 by Bird et al.[10] demonstrates the efficacy of chemotherapy in patients with fungating MCC who already have adequate performance status, as well as the return to functionality following chemotherapy. While these articles discuss the illness burden of fungating MCC in its other guises of malodour and loss of locomotive functionality, there is a dearth in the literature regarding pain management in this malady.
A strength of this case report is that it describes this gentleman’s wound and pain management in depth and details the dressing regimen comprehensively. In retrospect, however, it might have been interesting to measure PROMs in this patient over a timeframe, such as his mood and pain levels, which would have made the purported improvement in his symptoms easier to visualise. Such PROMs could have been delineated on graphs or undergone statistical analyses like a Student’s t-Test to detect whether the improvement in quality of care was statistically significant. Nonetheless, alongside depicting this gentleman’s story, a key purpose of this study was to exercise the readership’s skills in differential diagnosis, which we believe we have fulfilled.
CONCLUSION
This case report is the first to report on fungating head and neck MCC wounds and does so in the context of palliative care. The report demonstrates the unlikely yet reasonable aetiology of tension headache in contributing to pain and the successful use of anticipatory lorazepam in symptomatic relief of pain radiation, nausea, and trait anxiety. In addition, the case demonstrates the specialist’s use of purposeful wound dressing to reduce the effects of stagnant exudate, which included leakage, pain, and irritation. The key takeaway of this report was the importance of considering other causes of headaches, other than the obvious nociception, to come to a working diagnosis.
Ethical approval
Ethical advice was sought from the University of Leicester Research Ethics Governance and Integrity Office, who deemed this report not to require ethical approval. In tandem, the NHS HRA Online Tool deemed this report not to require approval on their end either.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (A.I.)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (A.I.)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using A.I.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Fungal Cell Biology and Development In: Watkinson SC, Boddy L, eds. The Fungi (3rd ed). Academic Press; 2016. p. :37-66. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123820341000025 [Last accessed on 2023 Sep 18]
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A Novel Player in the Field: Merkel Disc in Touch, Itch and Pain. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:1412-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Skin Cancer Foundation. 2023. Available from: https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/merkel-cell-carcinoma/#:~:text=A%20Rare%2C%20Aggressive%20Skin%20Cancer&text=Merkel%20cell%20carcinoma%20(MCC)%20is%2040%20times%20more%20rare%20than,and%20a%20weakened%20immune%20system [Last accessed on 2023 Sep 18]
- [Google Scholar]
- Available from: https://clch.nhs.uk/services/tissue-viability [Last accessed on: 2023 Sep 18]
- Managing Tension Headaches at Home: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. MedlinePlus. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000421.htm#:~:text=Gently%20massaging%20your%20head%20and,or%20acetaminophen%2C%20may%20relieve%20pain [Last accessed on 2023 Sep 18]
- [Google Scholar]
- Wound Pain and Wound Healing Biomarkers From Wound Exudate: A Scoping Review. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2020;47:559-68.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Two Cases of Fungating Endocarditis followed by Convalescence. Med Chir Trans. 1905;88:97-108.
- [Google Scholar]
- Successful Management of Malodor from Fungating Tumors using Crushed Metronidazole Tablets. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;6:26-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Advanced Merkel Cell Cancer and the Elderly. Ir J Med Sci. 2005;174:58-60.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







