Translate this page into:
Bibliometric Analysis of Indian Journal of Palliative Care from 1995 to 2022 using the VOSviewer and Bibliometrix Software
*Corresponding author: Rajashree Srivastava, Department of Psychology, School of Liberal Education, Galgotias University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. rajashree.srivastava_phd19@galgotiasuniversity.edu.in
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Srivastava R, Srivastava S. Bibliometric analysis of Indian journal of palliative care from 1995 to 2022 using the VOSviewer and Bibliometrix software. Indian J Palliat Care 2022;28:338-53.
Abstract
Introduction:
The Indian Journal of Palliative Care (IJPC) is an open-source, interdisciplinary and peer-reviewed journal started in 1994 that publishes high-quality articles in the field of palliative care in India. The purpose of this study is to analyse the bibliometric data of its publications using bibliometric analysis to understand the key bibliometric factors affecting the journal and its contribution to the field of palliative care research.
Material and Methods:
A software-assisted bibliometric analysis of the IJPC was conducted. The dimensions database was used to mine the bibliometric data of the journal from 1995 to 2022. A total of 1046 records were analysed using the VOSviewer and Biblioshiny by Bibliometrix software.
Results:
The analysis represented a vivid and graphically elaborate picture of the journal. It gives insight into the most productive and influential authors, countries, affiliations, sources and documents along with a picture of the network among them.
Conclusion:
This study highlights a gradual upward trend in the annual production of the journal. A strong connection of the IJPC could be seen with leading journals publishing in the field of palliative care globally.
Keywords
Bibliometrics
Visual mapping
VOSviewer
Single journal study
Indian journal of palliative care
INTRODUCTION
The Indian Journal of Palliative Care (IJPC), started in 1994, is an open-access, interdisciplinary and peer-reviewed journal that publishes high-quality articles in the field of palliative care quarterly.[1] Owned by the Indian Association of Palliative care and published by scientific scholar, the journal is indexed by PubMed Central, SCOPUS, Emerging Sources Citation Index, Indian Science Abstracts and Scimago Journal Ranking.[1] At present, the editorial comprises Dr. Raghavendra Ramanjulu as the editor.[1]
Considering the IJPC is the only impact factor journal dedicated to research in palliative care and its multidisciplinary fields in India, it becomes of special interest for the bibliometric analysis. The method is a mathematical and statistical approach to analyse bibliographic data of books, journals and scientific papers.[2] It gives an insight into the emerging trends in a particular area of research, research themes, journal performance, research constituents and collaboration networks.[3] The bibliometric study could be used to analyse the publication patterns of written communication in a specific field of research including data from multiple sources or it could be a single journal study. However, single journal studies, in particular, contribute insights into the productivity and quality of the journal in a specific field, providing a detailed multifaceted picture of the characteristics of the journal.[4,5] Single journal studies using the bibliometric approach have been applied to other disciplines such as humanities, health and medicine, science and technology library sciences, economics and management studies.[5]
Since the IJPC is significant to the field of palliative care research, specifically in India, the analysis is essential to increase understanding of the research activity in the area. Hence, to understand the research trends of palliative care research in India from various bibliometric indicators and to gain insights into the top contributors in the field, an in-depth analysis of the journal’s bibliometric properties is required. The analysis also becomes significant considering no single journal bibliometric analysis or scientific mapping could be found of the IJPC through the literature review to the best of our knowledge.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The main objective of the study is to conduct a bibliometric analysis and scientific mapping of the IJPC. The study would cover the following analysis:
Data analysis of the publication output
Citation analysis
Authorship analysis
Network analysis among documents, authors, affiliation, text and countries along with bibliometric coupling
Identifying major research trends through a multiphasic study.
METHOD AND MATERIALS USED
This study focuses on the bibliometric analysis of publications by the IJPC. Donthu et al. in their paper, ‘How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines.’ Have proposed a four-step procedure for conducting bibliometric analysis?[6] The steps include: (1) Define the aim and scope of the bibliometric study, (2) choose the technique, (3) collect the data and (4) run the bibliometric data and report findings. This research is in line with the suggested four-step procedure. The Dimensions database was used to extract data for the bibliometric analysis. The Source Title was limited to the ‘Indian Journal of Palliative Care (IJPC),’ whereas the Publication type was limited to ‘Articles.’ A total of 1049 records from the year ‘2005 to 2022’(last accessed on January 19, 2022) were downloaded in CSV format. The exported data were then run in the selected software. For our analysis, we used the VOSviewer and Bibliometrix software.
Biblioshiny app by Bibliometrix is an open-source, R tool that requires no coding for the analysis of data.[7] Following analysis of the IJPC data was done through the Bibliometrix software.
Dataset analysis
Citation analysis
Authorship analysis
Conceptual structure and thematic analysis.
VOSviewer is open-source software that creates and represents network visualisation maps.[8] The software was primarily used to create network maps and relationships between the bibliometric data. The software employs a technique that helps the users construct and view distance-based maps in which the distance between two items reflects the strength and relationship between the selected items. Following analysis of the IJPC data was run through the VOSviewer software.
Cocitation network
Coauthorship network
Bibliographic coupling
Cooccurrence map based on text data.
DATA ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
In this study, 1049 articles were identified and extracted from the dimensions database. The extraction included all the articles published between 2005 and 2022.
Data set analysis
[Table 1] represents the main information about the data collected, while [Table 2] represents the annual scientific production of the journal. In the beginning year 2005, a total of 25 articles were published, the number decreasing to 14 in the year 2007 but after that, there was a gradual and steady rise in the number of articles published. Years 2018–2021 were the highest productive years of IJPC, whereas in the year 2020, maximum articles were published; 150 articles in total. A total of 2356 articles were published in the journal among which, 133 were single-authored documents and 2223 were multi-authored documents.
| Description | Results |
|---|---|
| Main information about the Indian Journal of Palliative Care | |
| Timespan | 2005:2022 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc.) | 1 |
| Documents | 1049 |
| Average years from publication | 6.24 |
| Average citations per document | 6.308 |
| Average citations per year per doc | 0.782 |
| References | 15085 |
| Document types | |
| Article | 1049 |
| Document contents | |
| Keywords plus (ID) | 1 |
| Author’s keywords (DE) | 1 |
| Authors | |
| Authors | 2356 |
| Author Appearances | 3923 |
| Authors of single-authored documents | 133 |
| Authors of multi-authored documents | 2223 |
| Authors collaboration | |
| Single-authored documents | 203 |
| Documents per author | 0.445 |
| Authors per document | 2.25 |
| Coauthors per documents | 3.74 |
| Collaboration Index | 2.68 |
| Year | Articles |
|---|---|
| 2005 | 25 |
| 2006 | 16 |
| 2007 | 14 |
| 2008 | 17 |
| 2009 | 32 |
| 2010 | 37 |
| 2011 | 75 |
| 2012 | 39 |
| 2013 | 45 |
| 2014 | 52 |
| 2015 | 72 |
| 2016 | 83 |
| 2017 | 79 |
| 2018 | 106 |
| 2019 | 98 |
| 2020 | 150 |
| 2021 | 104 |
| 2022 | 5 |
[Table 2 and Figure 1] represent the annual scientific production of the journal. A steady and upward trend in the annual scientific publication of the journal could be seen through the graphical representation in [Figure 1].
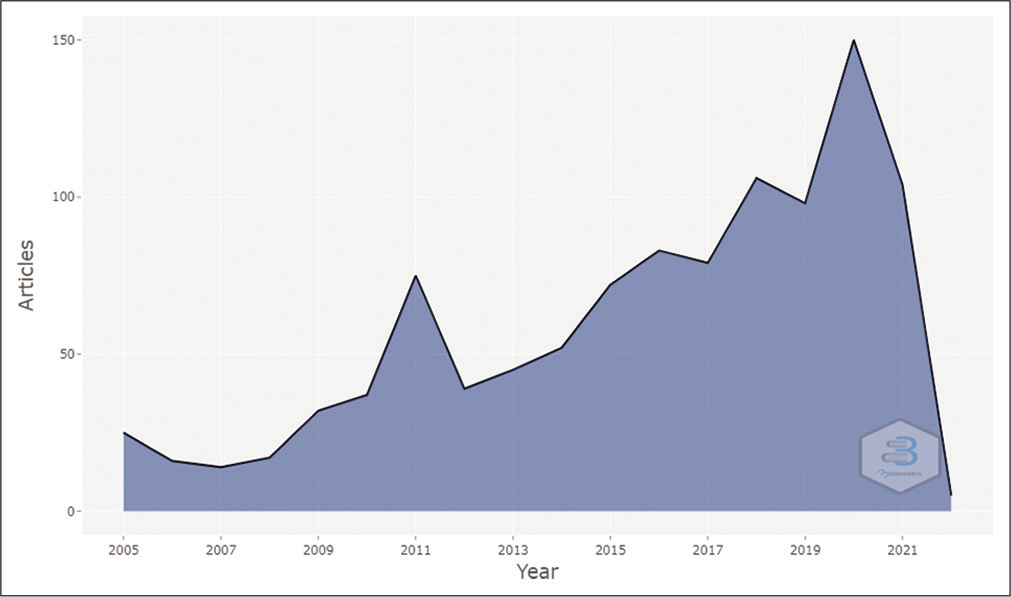
- Annual scientific production (analysis done through Bibliometrix software).
Sources analysis
An analysis of locally cited sources reported that a total of 2761 sources were cited in the IJPC. [Table 3] represents the top 20 locally cited sources; sources that were cited within the IJPC, whereas [Figure 2] is the graphical representation of the top 20 locally cited sources. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management is the most cited source in the cited references of articles published in IJPC, cited in 748 articles, followed by the Indian Journal of Palliative Care itself, locally cited in 680 articles and journal of Clinical Oncology and Palliative Medicine cited in 428 and 426 articles, respectively.
| Sources | Articles |
|---|---|
| Journal of pain and symptom management | 748 |
| Indian journal of palliative care | 680 |
| Journal of clinical oncology | 428 |
| Journal of palliative medicine | 426 |
| Palliative medicine | 409 |
| Supportive care in cancer | 385 |
| Cancer | 351 |
| Pain | 285 |
| Psycho-oncology | 235 |
| American journal of hospice and palliative medicine® | 212 |
| The BMJ | 205 |
| The LANCET | 197 |
| JAMA | 191 |
| Annals of oncology | 175 |
| New England journal of medicine | 175 |
| International journal of radiation oncology • Biology • Physics | 154 |
| Cochrane database of systematic reviews | 153 |
| Cancer nursing | 123 |
| European journal of cancer | 119 |
| Journal of advanced nursing | 116 |
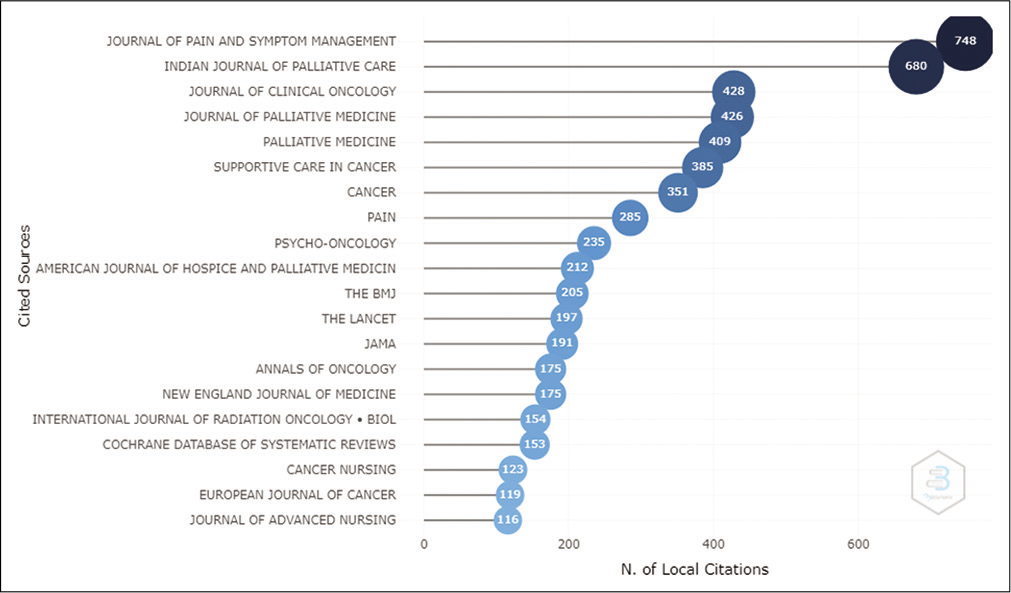
- Graphical representation of most local cited sources.
Authorship analysis
[Figure 3] represents the top 20 most relevant authors in IJPC. Most relevant authors refer to the authors with the highest number of articles published in the journal. As represented in [Figure 3], Bhatnagar S ranks first with a total count of 113 publications followed by Salins N contributing 46 publications and Mishra S with a total of 33 publications. In line with top authors, [Figure 4] represents the top 20 author’s production over time in terms of the number of publications and citations per year. The bubbles represent the number of articles published by a particular author in a given period. The darker and bigger the bubble is in a particular timeline, the most productive the author had been that year. [Figure 4] suggests that the year 2020 had been the most productive for most of the authors.
[Table 4] represents the 20 top authors with the number of publications, and total citations according to h-index, g-index and m-index. The h-index is an author-level metric that measures the author’s production and citation impact whereas the m-index is the h-index divided by the active years of a particular author.

- Most relevant author.

- Top author’s production over time.
| Element | h_index | g_index | m_index | TC | NP | PY_start |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhatnagar S | 12 | 17 | 0.857 | 477 | 78 | 2009 |
| Kumar SP | 9 | 17 | 0.692 | 327 | 21 | 2010 |
| Mishra S | 7 | 11 | 0.5 | 152 | 26 | 2009 |
| Rassouli M | 7 | 8 | 0.778 | 169 | 8 | 2014 |
| Salins N | 7 | 12 | 0.583 | 214 | 32 | 2011 |
| Chaturvedi SK | 6 | 13 | 0.375 | 186 | 13 | 2007 |
| Kumar S | 6 | 9 | 0.333 | 109 | 18 | 2005 |
| Muckaden M | 6 | 9 | 0.5 | 105 | 15 | 2011 |
| Rao RM | 6 | 6 | 0.75 | 100 | 6 | 2015 |
| Deodhar J | 5 | 8 | 0.625 | 79 | 11 | 2015 |
| Garg R | 5 | 6 | 0.455 | 54 | 12 | 2012 |
| Ghoshal A | 5 | 5 | 0.625 | 61 | 17 | 2015 |
| Gupta M | 5 | 6 | 0.455 | 69 | 6 | 2012 |
| Kulkarni P | 5 | 5 | 0.556 | 128 | 5 | 2014 |
| Mohanti BK | 5 | 5 | 0.357 | 86 | 5 | 2009 |
| Muckaden MA | 5 | 10 | 0.278 | 109 | 14 | 2005 |
| Patil S | 5 | 5 | 0.625 | 94 | 5 | 2015 |
| Rahmani A | 5 | 5 | 0.556 | 79 | 5 | 2014 |
| Ahmed A | 4 | 7 | 0.333 | 69 | 7 | 2011 |
| Atreya S | 4 | 6 | 0.571 | 39 | 6 | 2016 |
[Figure 5] suggests the top 20 relevant affiliations. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) is the top relevant affiliation with a total of 97 articles published in IJPC by different authors followed by TATA memorial hospital with a count of 90 documents and DR. B.R. Ambedkar Institute Rotary Cancer Hospital with a count of 52 documents.

- Most relevant affiliations.
[Table 5] suggests the corresponding author’s country’s scientific production. India, Iran and the UK are the top 3 countries with the most scientific productions, the number of documents being 843, 146 and 44, respectively, whereas, [Table 6] suggests the most cited countries. [Figure 6] is the graphical representation of [Table 5].
| Region | Freq |
|---|---|
| India | 843 |
| Iran | 146 |
| UK | 44 |
| Australia | 27 |
| Canada | 25 |
| Sweden | 20 |
| Italy | 19 |
| Japan | 15 |
| Turkey | 15 |
| Greece | 13 |
| Egypt | 12 |
| Indonesia | 12 |
| Saudi Arabia | 12 |
| Malaysia | 10 |
| Nigeria | 10 |
| Singapore | 10 |
| South Africa | 6 |
| China | 5 |
| Colombia | 5 |
| Germany | 5 |
| Country | Total citations | Average article citations |
|---|---|---|
| India | 3573 | 5.867 |
| Iran | 917 | 12.392 |
| Na | 906 | 5.491 |
| United Kingdom | 169 | 7.042 |
| United States | 115 | 4.423 |
| Nigeria | 93 | 18.6 |
| Canada | 90 | 9 |
| Nepal | 77 | 38.5 |
| Australia | 73 | 6.636 |
| Belgium | 62 | 15.5 |
| Jordan | 52 | 26 |
| Singapore | 50 | 8.333 |
| Indonesia | 43 | 5.375 |
| Morocco | 39 | 19.5 |
| Italy | 38 | 4.75 |
| New Zealand | 29 | 9.667 |
| Thailand | 29 | 9.667 |
| Japan | 27 | 3.857 |
| Malaysia | 25 | 2.778 |
| Pakistan | 24 | 12 |
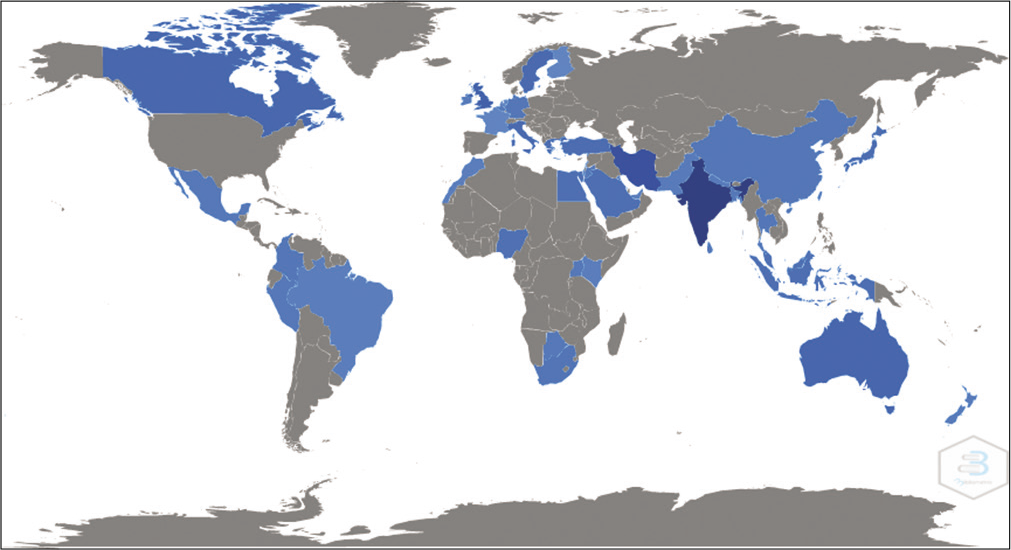
- Country’s scientific production.
Citation analysis
[Table 7] represents the top 20 globally cited documents, with the paper by Khosla et al., named Palliative Care in India: Current Progress and Future Needs, published in the year 2012 being cited 81 times globally,[9] followed by Chaturvedi et al.[10] cited 76 times and Narayan et al. (2010) cited 72 times.[11-28]
| Paper | Document | Total citations | TC per Year | Normalised TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khosla et al., 2012[9] | Palliative Care in India: Current Progress and Future Needs | 81 | 7.3636 | 5.2129 |
| Chaturvedi et al., 2009[10] | Communication with Relatives and Collusion in Palliative Care: A Cross-cultural Perspective | 76 | 5.4286 | 5.0667 |
| Narayanan et al., 2010[11] | ‘BREAKS’ Protocol for Breaking Bad News | 72 | 5.5385 | 5.4037 |
| Anaraki et al., 2012[12] | Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients Living with Stoma | 64 | 5.8182 | 4.1188 |
| Zamanzadeh et al., 2015[13] | Effective Factors in Providing Holistic Care: A Qualitative Study | 63 | 7.875 | 6.4615 |
| Nayak et al., 2017[14] | Quality of Life among Cancer Patients | 62 | 10.3333 | 7.4325 |
| Kumar, 2011[15] | Utilisation of Brief Pain Inventory as an Assessment Tool for Pain in Patients with Cancer: A Focused Review | 61 | 5.0833 | 5.6273 |
| Somasundaram and Devamani, 2016[16] | A Comparative Study on Resilience, Perceived Social Support and Hopelessness Among Cancer Patients Treated with Curative and Palliative Care | 56 | 8 | 6.6117 |
| Hatamipour et al., 2015[17] | Spiritual Needs of Cancer Patients: A Qualitative Study | 56 | 7 | 5.7436 |
| Kumar and Jim 2010[18] | Physical Therapy in Palliative Care: From Symptom Control to Quality of Life: A Critical Review | 52 | 4 | 3.9026 |
| Jafari et al., 2015[19] | Caring for Dying Patients: Attitude of Nursing Students and Effects of Education | 51 | 6.375 | 5.2308 |
| Zamanzadeh et al., 2014[20] | Factors Influencing Communication Between the Patients with Cancer and their Nurses in Oncology Wards | 46 | 5.1111 | 5.9355 |
| Lambert and Lambert 2008[21] | Nurses’ workplace stressors and coping strategies | 46 | 3.0667 | 4.2732 |
| Melhem et al., 2016[22] | Nurses’ Perceptions of Spirituality and Spiritual Care Giving: A Comparison Study Among All Health Care Sectors in Jordan | 45 | 6.4286 | 5.3129 |
| Singh and Chaturvedi, 2015[23] | Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Cancer Pain Management: A Systematic Review | 45 | 5.625 | 4.6154 |
| Sabo, 2008[24] | Adverse psychosocial consequences: Compassion fatigue, burnout and vicarious traumatisation: Are nurses who provide palliative and haematological cancer care vulnerable? | 45 | 3 | 4.1803 |
| Kumar and Numpeli, 2005[25] | Neighbourhood network in palliative care | 45 | 2.5 | 6.1475 |
| Satheesh Kumar et al., 2009[26] | Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis | 44 | 3.1429 | 2.9333 |
| Jacobsen et al., 2006[27] | Depression and demoralisation as distinct syndromes: Preliminary data from a cohort of advanced cancer patients | 44 | 2.5882 | 7.2577 |
| Prem et al., 2012[28] | Study of Nurses’ Knowledge about Palliative Care: A Quantitative Cross-sectional Survey | 42 | 3.8182 | 2.703 |
TC: Total citation
Research trends
Studying the research trends of a particular journal help researchers and the general readers of the publication identify the key areas of interest in a particular field of research. It gives an insight into research themes explored over the given years, helping scholars to track and trace these research trends and contribute further to the research field.
To understand the key areas of research and major themes, the bibliometric data were divided into three phases based on the year of publication. Phase I covered the publications from the year 2005 to 2010, Phase II covered the publications from the year 2011 to 2016 and Phase III covered the publications from the year 2017 to 2022 (till January 2022).
Phase I (2005–2010)
A total of 141 articles were published during this phase. Conceptual structure analysis using the Bibliometrix software was done to create a thematic map of the research trends during this phase. The parameter was set to ‘Author’s Keywords’ where trends were identified through the frequency of occurrence of a keyword. The frequently occurring themes during this phase were palliative care research in quality of life, cancer pain, pain, community home-based program, breaking bad news and communication among others. [Table 8] represents the thematic map data.
| Occurrences | Keywords | Cluster | Cluster_Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | Palliative care | 2 | Palliative care |
| 6 | Quality of life | 8 | Quality of life |
| 5 | Cancer pain | 7 | Cancer pain |
| 4 | Pain | 4 | Pain |
| 4 | HIV/AIDS | 5 | HIV/AIDS |
| 4 | Cancer | 6 | Cancer |
| 3 | Community home-based care program | 5 | HIV/AIDS |
| 2 | Chemotherapy | 1 | Chemotherapy |
| 2 | Radiotherapy | 1 | Chemotherapy |
| 2 | Awareness | 2 | Palliative care |
| 2 | Euthanasia | 2 | Palliative care |
| 2 | breaking bad news | 3 | Breaking bad news |
| 2 | Communication | 3 | Breaking bad news |
| 2 | Care giving | 5 | HIV/AIDS |
| 2 | Palliative caregivers | 5 | HIV/AIDS |
| 2 | Perfidy | 5 | HIV/AIDS |
| 2 | Oral morphine | 7 | Cancer pain |
| 2 | palliative radiotherapy | 7 | Cancer pain |
| 2 | Rehabilitation | 8 | Quality of life |
| 2 | Oncology | 9 | Oncology |
Further, a thematic map was created to understand the major themes dividing them into the quadrants of four themes: Basic, motor, niche and emerging themes. The parameter was again set to research keywords as given by authors.
Basic Themes: Basic themes identified were cancer pain, palliative radiotherapy, oral morphine, quality of life and rehabilitation. Euthanasia and awareness were covered to some extent as well
Motor Themes: Motor themes identified were cancer, communication, breaking bad news and oncology
Niche Themes: Niche themes identified were HIC/AIDS, community-based care programs and caregiving.
Emerging Themes: Emerging themes during this phase were chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
[Figure 7] represents the thematic map of the themes during this period.

- Thematic map of research themes.
[Figure 8] represents the word cloud generated out of the published titles in the journal during this phase exploring the major themes through the titles of the research.
- Word Cloud (Published titles).
Phase II (2011–2016)
Publications were significantly increased with a total of 366 documents published during this phase. A frequency trend of research topics through the author’s keywords was analysed using thematic mapping where 13 major themes were identified and divided into clusters. These major research themes or clusters were then divided into sub-themes. It was also noticed that during this phase, there was a significant increase in research related to the psychosocial effects of cancer. Furthermore, a significant number of studies came from the country Iran.
Major research themes in this period were cancer pain, chemotherapy, radiotherapy in head-and-neck cancer and supportive care along with an increased focus on psychosocial aspects of palliative care.
Major clusters and sub-themes identified in the clusters are represented in [Table 9], along with their frequency of occurrence.
| Cluster name | Words (Sub themes) | Frequency of Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| Palliative Care | Home-based Care End-of-life Care |
5 |
| Palliative Care | Culture, euthanasia, networking haematological malignancies and squamous cell carcinoma | 3 |
| Palliative Care | End-stage renal disease, hyponatremia, maxillectomy, outpatient, palliative medicine, peritoneal dialysis, Saudi Arabia, sickle cell disease, symptom burden, training, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, challenges, delirium, education, dyspnoea, morphine and cervix | 2 |
| Quality of Life | Chronic pain, Research | 4 |
| Quality of Life | Concurrent chemoradiotherapy, oesophageal cancer, evidence-based palliative care, fact-g, home-based palliative care, journal reporting, perception, publication trend and reliability | 2 |
| Radiotherapy | Chemotherapy | 8 |
| Radiotherapy | Head-and-neck Cancer and Supportive Care | 6 |
| Radiotherapy | Fatigue, palliation and physical therapy | 3 |
| Radiotherapy | Adolescents, mechanism-based classification, non-compliance, pain rehabilitation, palliative oncology and treatment | 2 |
| Zoledronic acid | Zoledronic acid | 2 |
| Pain Management | Children, complications, leukaemia and neuropathic pain | 2 |
| Nursing Education | Nursing education and pain assessment | 2 |
| Knowledge | Breast Cancer | 6 |
| Knowledge | Attitude and end-of-life | 5 |
| Knowledge | Terminally ill | 3 |
| Knowledge | Awareness, breast self-examination opioids, South India |
2 |
| Iran | Nurses | 6 |
| Iran | Cancer Patient and Social Support | 5 |
| Iran | Attitudes, developing countries Qualitative study and Spirituality |
4 |
| Iran | Audit, palliative sedation, end-of-life hospice care, human immunodeficiency virus, multiple sclerosis and physicians self-concept | 2 |
| India | Old-age | 4 |
| India | Cultural | 3 |
| India | Caregivers, communication, family, holistic care multidisciplinary team, psychological, rural, social, survivors, team approach and total pain | 2 |
| Cancer Pain | Palliative Radiotherapy | 4 |
| Cancer Pain | North-west India, interventions, metronomic chemotherapy, opioid dependence, oral morphine, regional cancer centre, sociodemographic parameters, substance abuse and therapeutic nihilism | 2 |
| Cancer | Pain | 15 |
| Cancer | Depression, Oncology and Stress | 6 |
| Cancer | Communication skills and symptoms | 3 |
| Cancer | Anxiety, breaking bad news, critically ill Distress, early specialist palliative care, gabapentin, intensive care unit, music, neuropathic, severe pain, truth-telling and yoga |
2 |
| Ampulla of Vater | Extrahepatic biliary obstruction, gall bladder carcinoma and periampullary growth | 2 |
[Figure 9] represents the thematic map of the major themes divided into four quadrants which were.
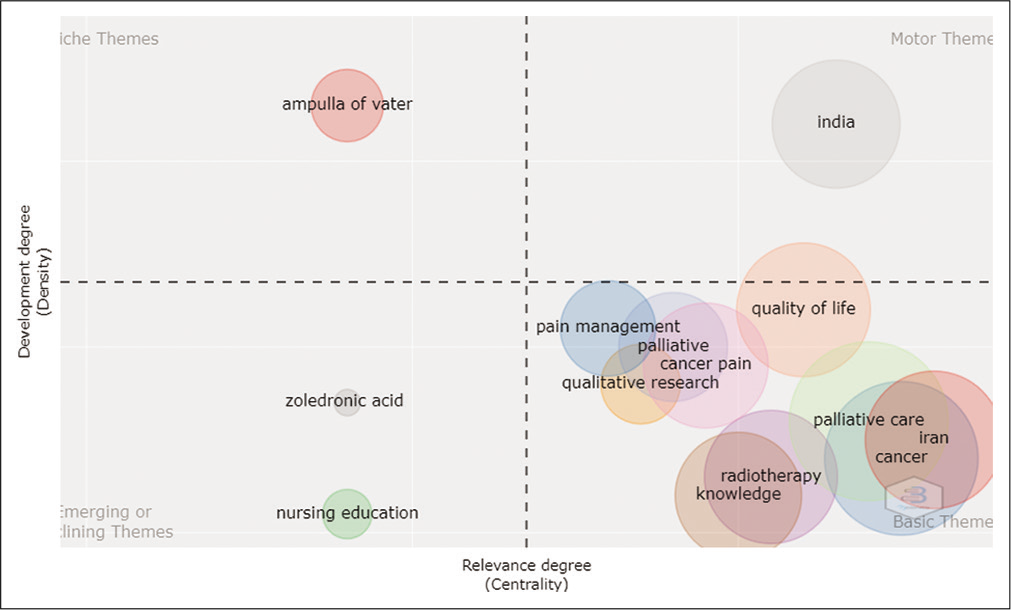
- Thematic Map (Phase II).
Basic Themes: Out of the 13 clusters, eight clusters were under basic themes. The basic themes were palliative care, Iran, radiotherapy, knowledge, cancer, cancer pain, quality of life and pain management
Motor Theme: The cluster heading India was identified as the motor theme
Niche Theme: Ampulla Of Valler was identified as the niche theme
Emerging Themes: Nursing education and Zoledronic acid were identified as emerging themes.
Phase III (2017–2022)
A total of 542 articles were published in this phase, more than twice the documents published in Phase I and Phase II combined. A thematic evolution study was done for this phase to detect and visualise the research themes and their evolution across 3-time periods. Assuming that this phase saw the rise of COVID-19-related research, we divided further divided this phase into three phases so to isolate the COVID-19-related studies from the rest of the research themes to get a clearer picture of research themes pre-COVID, during COVID and post-COVID period:
Time Slice 1 covered the data from 2017 to 2019 (the Pre-COVID phase)
Time Slice 2 covered the data for 2020. (The emergence of COVID-19)
Time Slice 3 covered the data from 2021-2022 (Post-COVID phase).
[Figure 10] is the snapshot of the thematic evolution where it could be observed that the primary research themes during Time slice 1 (2017–2019) were broadly pain-management, end-of-life care and psychosocial aspects of palliative care. In Time slice 2 (2020), the major themes were pandemic, methadone, quality of life and pain management, while in Time Slice 3 (2021–2022), major themes were cancer, anxiety and qualitative research.
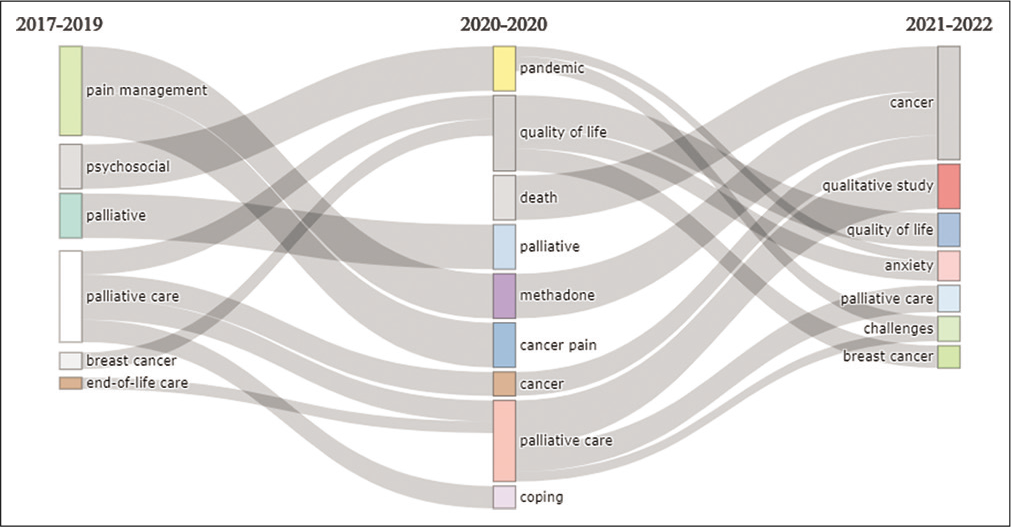
- Thematic Evolution.
Thematic analysis was done separately for the 3-time slices of this phase to get a broader idea of major research themes and sub-themes.
Time slice 1 (2017–2019)
Fifteen clusters or major research themes were identified during this phase. [Table 10] summarises the research themes in detail. In the line of the above data, [Figure 11] represents the thematic map of Time Slice 1.
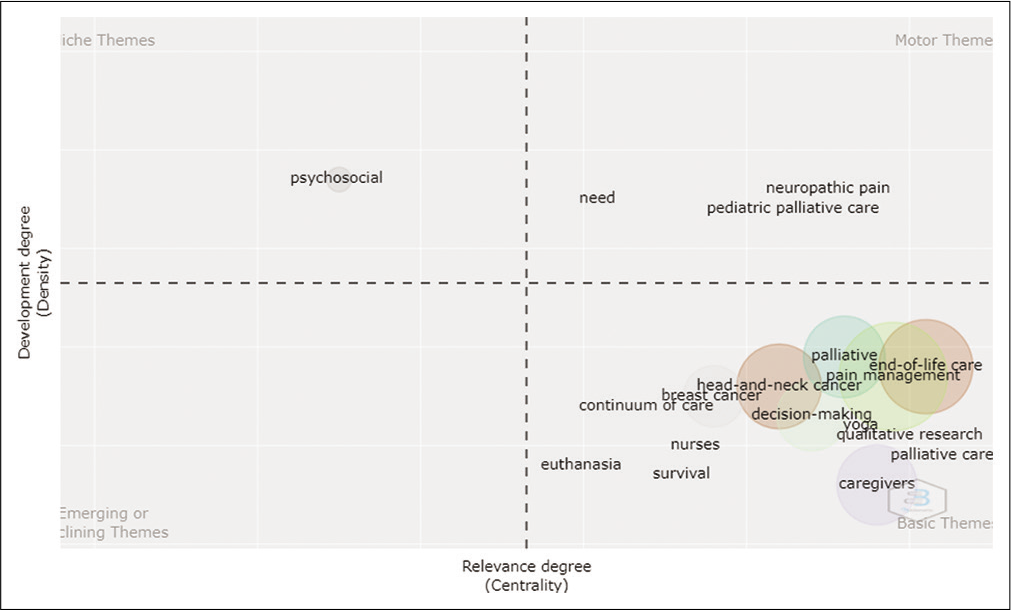
- Thematic Map (Time Slice 1- Phase III).
| Type of Theme | Research themes and Sub-themes |
|---|---|
| Basic Themes | End-of-life Care • End-of-life care in patients • Knowledge of End-of-life Care • Role of nurses in End-of-life care • Attitude, awareness and barriers in end-of-life care • Community-based palliative care and meaning of end-of-life care Caregiver Caregiver’s burden, home care and pain management Pain Management • India • Cancer pain • Methadone • Ketamine • Parents • Psychological effects Decision-making • Spiritual counseling • Education • Surrogates • Palliative medicine Qualitative research Qualitative research on advanced cancer, chronic pain, needs, dyspnoea and neck cancer Breast cancer Survival Survival in malignant pleural effusion Head-and-neck cancer • Opioid • Early Palliative Care Palliative care • Communication in Palliative Care • Collusion • Cancer pain • Psychosocial aspects • Quality of life in palliative care • Paediatric Palliative care • Spirituality • Mental Health Continuum of care Yoga Euthanasia |
| Motor Themes | Neuropathic pain Paediatric Palliative Care |
| Niche Themes | Psychosocial Research |
Time slice 2: (2020)
Nine major themes of research were prominent during this phase; pandemic, quality-of-life, death, cancer pain, coping, methadone, cancer pain management guidelines, cancer and palliative care.
[Table 11] summarises the research themes and sub-themes into basic, motor, niche and emerging research themes.
| Theme Type | Research Areas: Major and sub-themes |
|---|---|
| Basic themes | Palliative Care: • Palliative Care and COVID-19 • End-of-Life care in Palliative Care • Pain management • Home Care • Tele-medicine • Barriers in Palliative Care Quality-of-Life • Chemotherapy • Breast Cancer • Chronic Kidney disease • Anxiety, depression and Distress • Haemodialysis • Caregivers Cancer • Cancer pain • Albumin • Lung Cancer • Neuropathic pain • Pregabalin • Terminally ill Pandemic • COVID-19 • Challenges • Holistic Care • Community Participation • Psychosocial effects Cancer Pain Management Guidelines • Cancer pain special interest group • Celiac Plexus Neurolysis • Home-based palliative care • Hospice • Opioid Death Methadone |
| Motor Themes | Palliative Medicine Coping in Health-care Professionals |
In line with the table, [Figure 12] is the graphical representation of the thematic map of Time Slice 2 (2020).
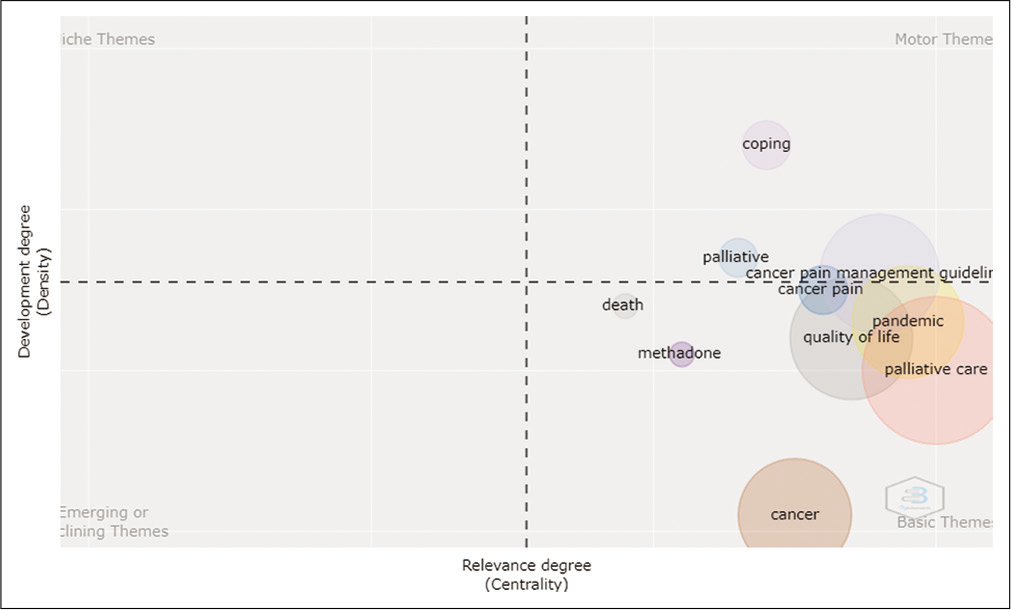
- Thematic Map Phase III Time Slice 2.
Time slice 3 (2021–2022)
Fifteen major themes (clusters) were identified during this phase. [Table 12] summarises the major themes and sub-themes during this phase.
| Type of Theme | Cluster_Label | Sub themes |
|---|---|---|
| Niche Themes | Psychosocial adjustment | Psychosocial adjustment |
| Stellate ganglion | Stellate ganglion | |
| Motor Themes | Quality of life | Quality of life |
| Quality of life | Head-and-neck cancer | |
| Quality of life | Haemodialysis | |
| Quality of life | Caregivers | |
| Breast cancer | Breast cancer | |
| Breast cancer | Distress | |
| Breast cancer | Psycho-oncology | |
| Breast cancer | Psychological distress | |
| Improvement | Improvement | |
| Improvement | Quality | |
| Anxiety | COVID-19 | |
| Anxiety | Depression | |
| Anxiety | Stress | |
| Basic Themes | Qualitative study | Qualitative study |
| Palliative medicine | Palliative medicine | |
| Palliative care | Palliative care | |
| Palliative care | Caregiver | |
| Palliative care | End-of-life care | |
| Palliative care | Advance care planning | |
| Palliative care | Attitude | |
| Palliative care | Chronic kidney disease | |
| Palliative care | Decision-making | |
| Palliative care | Dialysis | |
| Palliative care | Hospice care | |
| Palliative care | Mortality | |
| Palliative care | Shared decision-making | |
| Palliative care | Telemedicine | |
| India | India | |
| India | Quality improvement | |
| India | A3 methodology | |
| India | End-stage renal disease | |
| India | Neuropathic pain | |
| India | Questionnaire | |
| End-stage kidney disease | End-stage kidney disease | |
| End-stage kidney disease | Conservative care | |
| End-of-life | End-of-life | |
| Documentation | Documentation | |
| Challenges | Challenges | |
| Challenges | COVID-19 pandemic | |
| Challenges | Healthcare workers | |
| Challenges | Paediatric palliative care | |
| Cancer | Cancer | |
| Cancer | Pain | |
| Cancer | Methadone | |
| Cancer | Death | |
| Cancer | Grief | |
| Cancer | Mindfulness | |
| Cancer | Opioid |
In line with the above data, [Figure 13] is the representation of the thematic analysis.
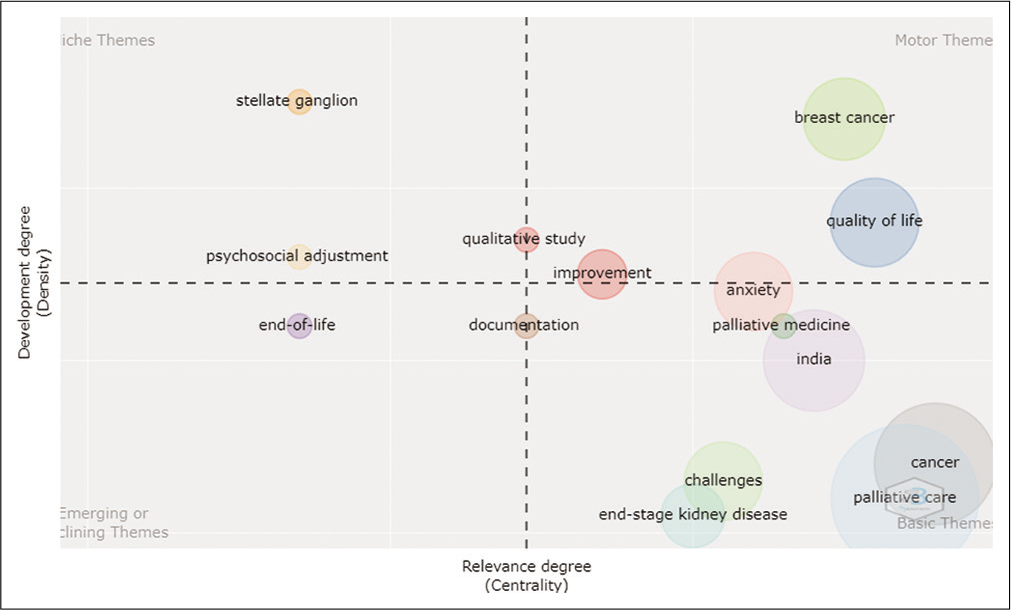
- Thematic Analysis (Time slice III).
Cocitation network
Cocitation refers to the frequency with which two documents are cited together with other documents.[29] [Figure 14] represents the cocitation network, the unit of analysis being sources where a cocitation network between the sources was established. The network map shows cocitation patterns of the 298 journals cited at least 10 times within the articles published in the journal we reviewed. In the figure, it could be seen that the biggest nodes and clusters belong to the IJPC and Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.
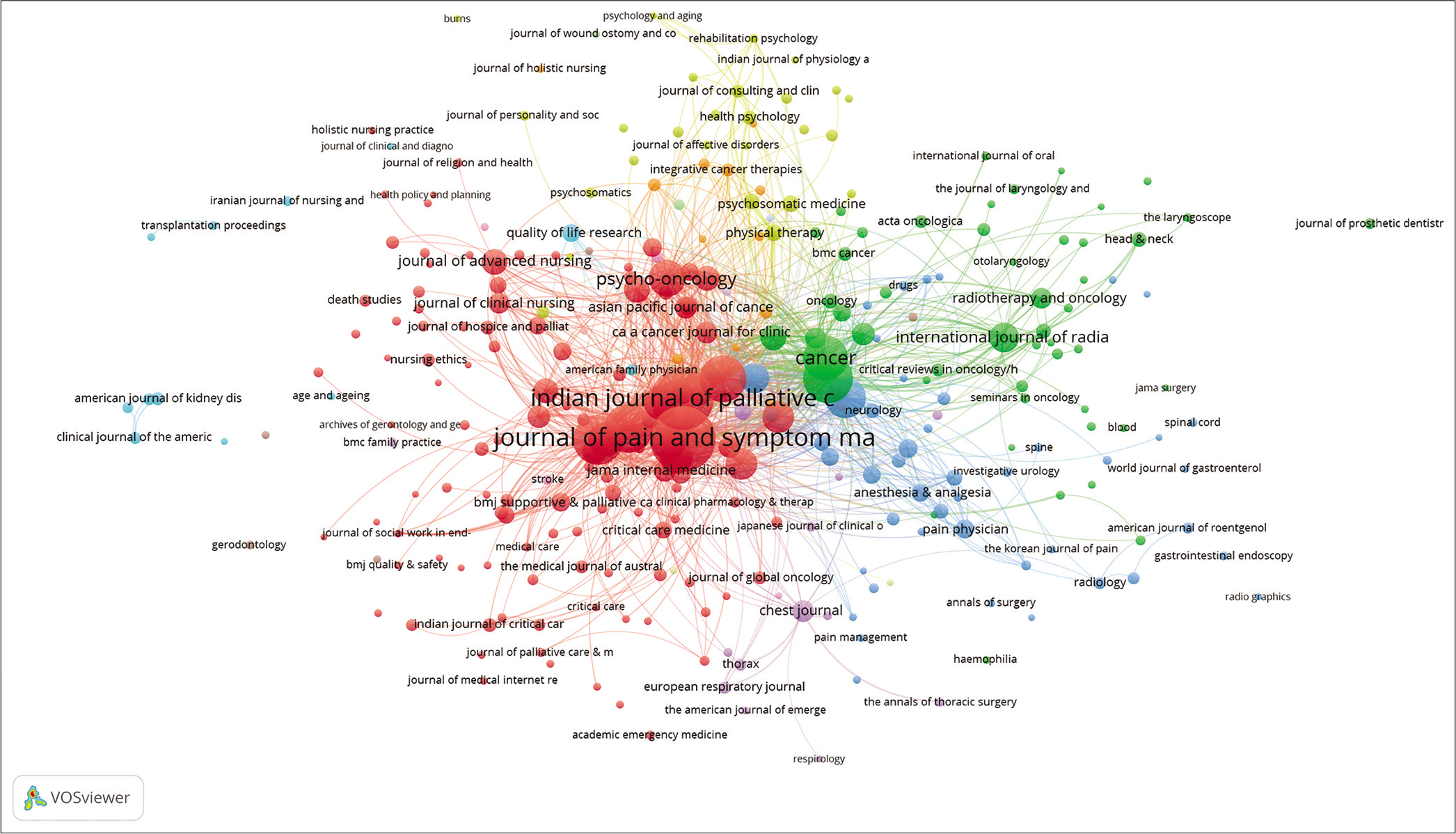
- Cocitation network between sources.
Coauthorship network
Coauthorship networks reflect the networks of collaboration between two or more authors of research work.[30] [Figure 15] represents the coauthorship network, the unit of analysis set to authors while the threshold was set to a minimum of two documents per author to measure the coauthorship network, which simply means that an author has to have published at least two articles in IJPC as the first author or co-author to be a part of the network map. Increasing the threshold would decrease the number of authors and clusters while decreasing the threshold would increase the number of authors and clusters in the network map. Publications with more than 25 authors were avoided to create viable network maps. Out of 2357 authors, 549 authors met the threshold and the largest network connection of authorship was of 382 items divided into 22 clusters, the biggest node being of the author Bhatnagar S. The different colours indicate the different clusters.
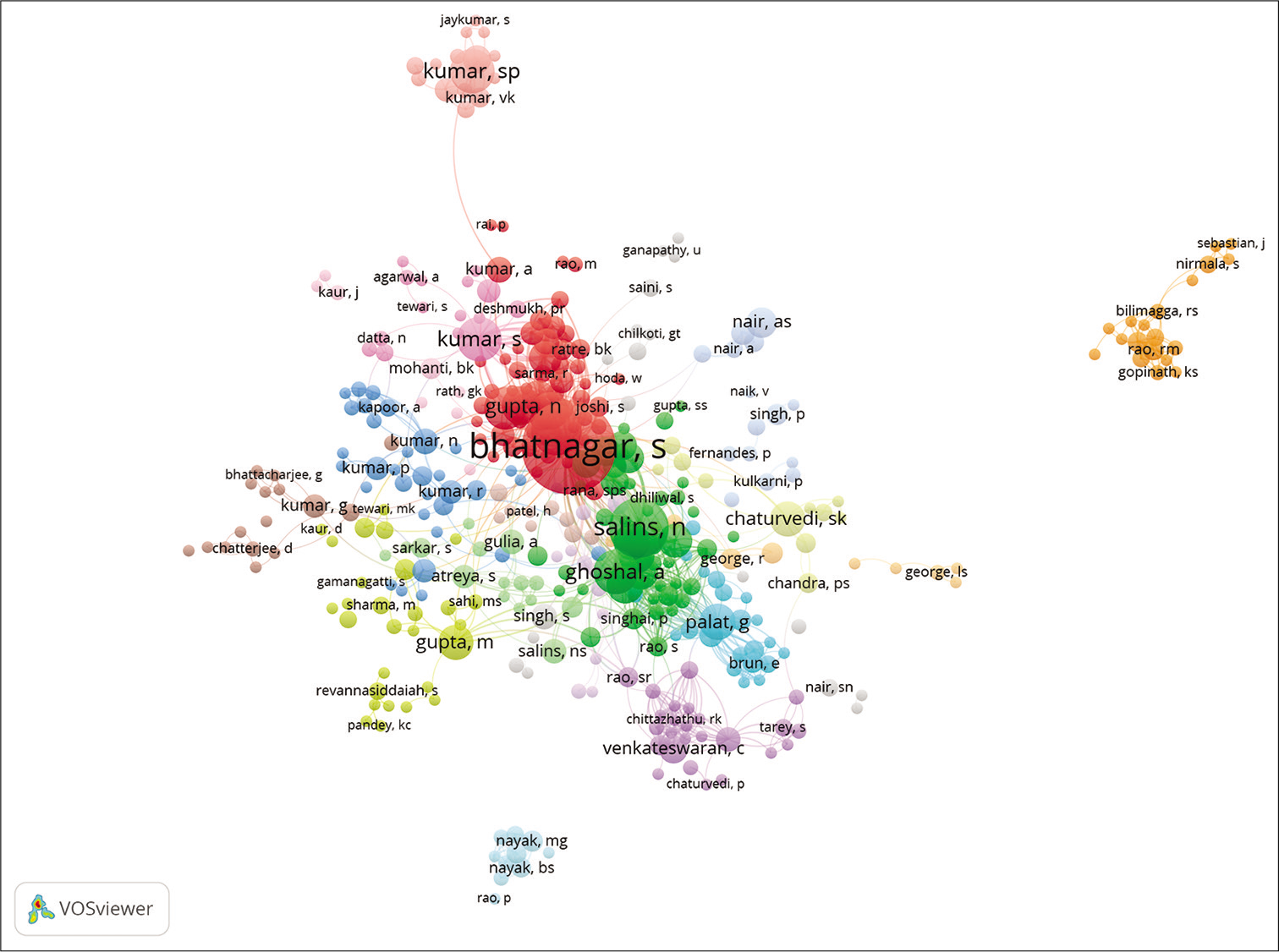
- Coauthorship network: Authors.
[Figure 16] represents the coauthorship network, the unit of analysis was set to ‘Country’, the threshold was set to a minimum of two articles published by the authors of a country. Forty-one countries met the threshold criteria. [Figure 9] depicts that India is taking a centre stage with the biggest node followed by Iran and U.K.
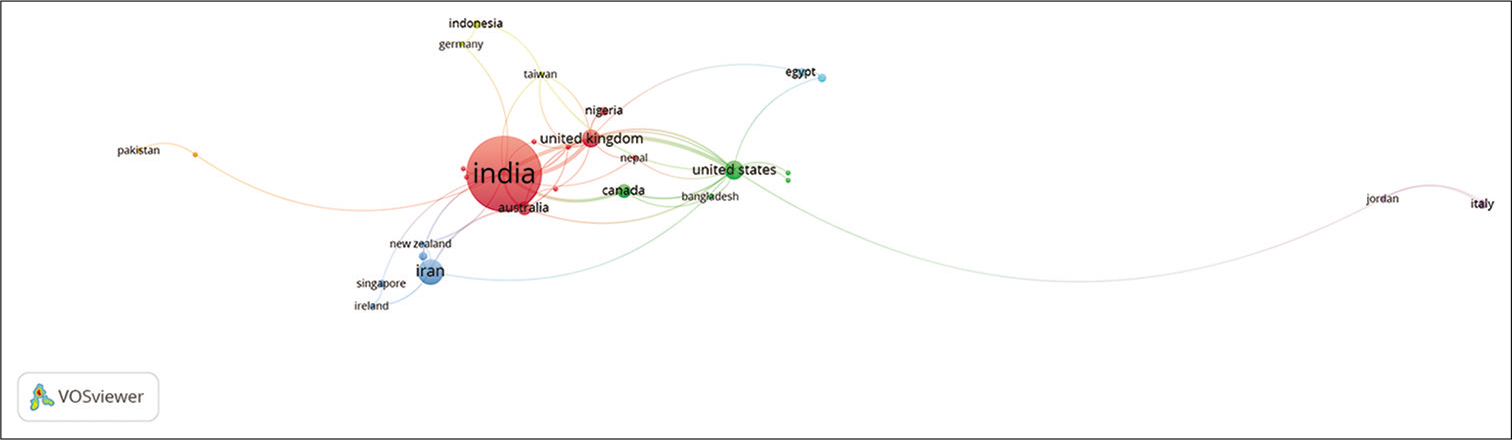
- Coauthorship network: Countries (Please find attached separately).
[Figure 17] represents the coauthorship networks concerning their affiliations. The unit of analysis was set to ‘organisation’. The threshold was set to a minimum of five documents per organisation. Out of 484 organisations, 53 met the threshold and the largest set of connected nodes was 35 organisations. AIIMS and Tata memorial hospital are the two central nodes with the biggest networks.
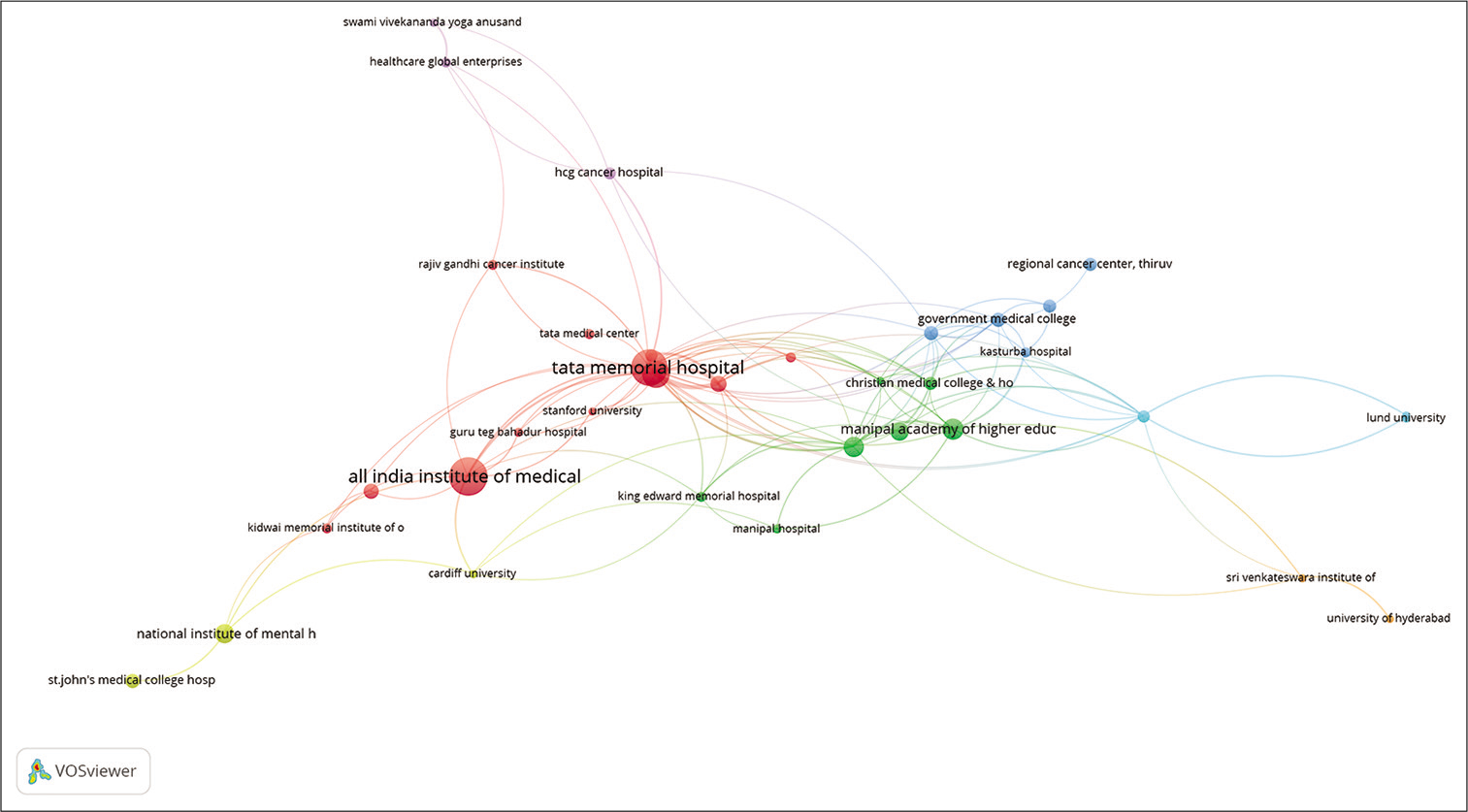
- Coauthorship network: Affiliations (Organisations).
Bibliographic coupling
When two works reference a common third work in their respective bibliographies, bibliographic coupling occurs.[31] Bibliographic coupling is done to map the relationship between documents, sources, authors, organisations and countries. [Figure 18] is the density map of bibliographic coupling, the unit of analysis was documents. The threshold was set to at least three citations per document, 531 documents met the threshold out of which 419 documents had the largest set of connections. The density visualisation best represented the coupling instead of network visualisation. The density around the document, Khosla D, (2012), Nayak SK, (2017) and Chaturvedi SK, (2009), is the denser areas as represented in [Figure 18].
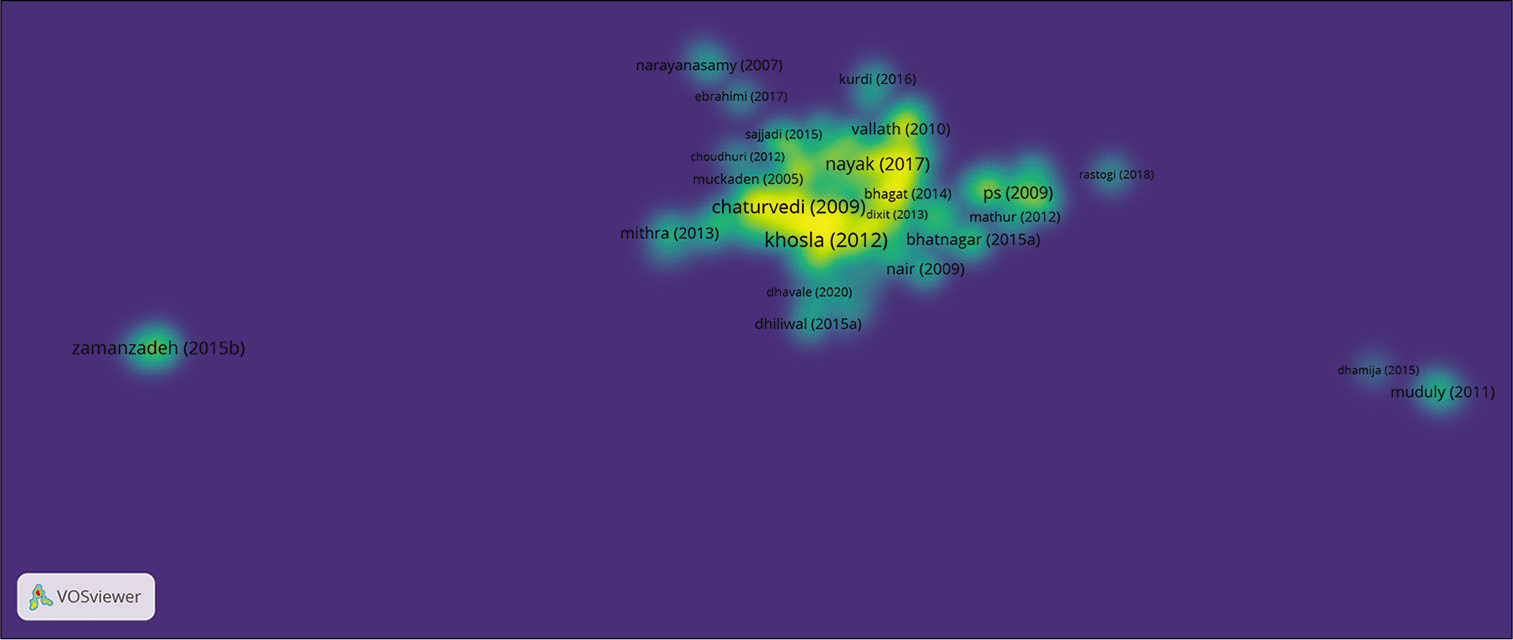
- Bibliographic coupling: Documents.
[Figure 19] represents the bibliographic coupling between authors. The threshold was set to at least five documents produced by an author. Out of 2577 authors, 71 met the threshold.
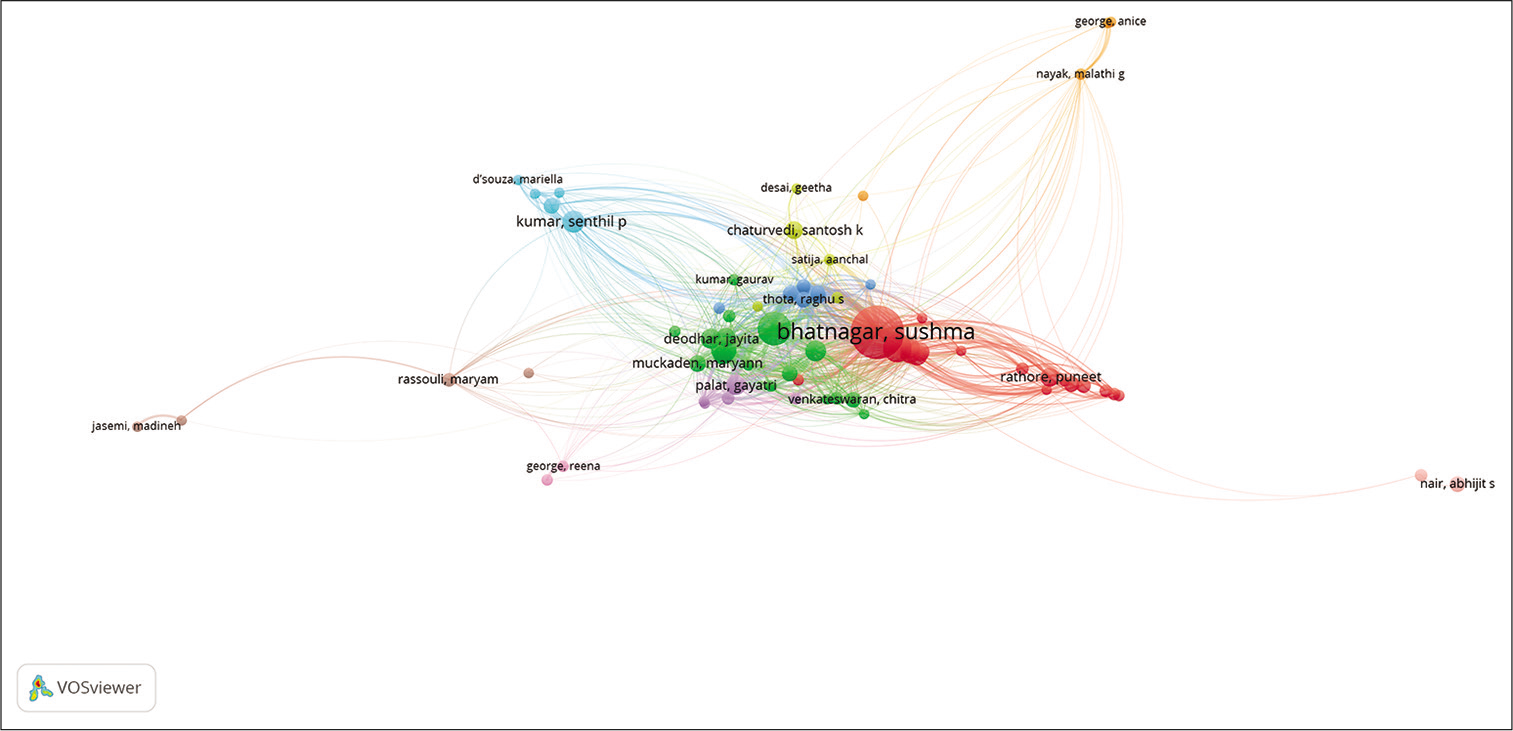
- Bibliographic coupling: Authors (Please find attached separately).
[Figure 20] represents the bibliographic coupling between affiliations. The unit of analysis is organisations (Affiliations).
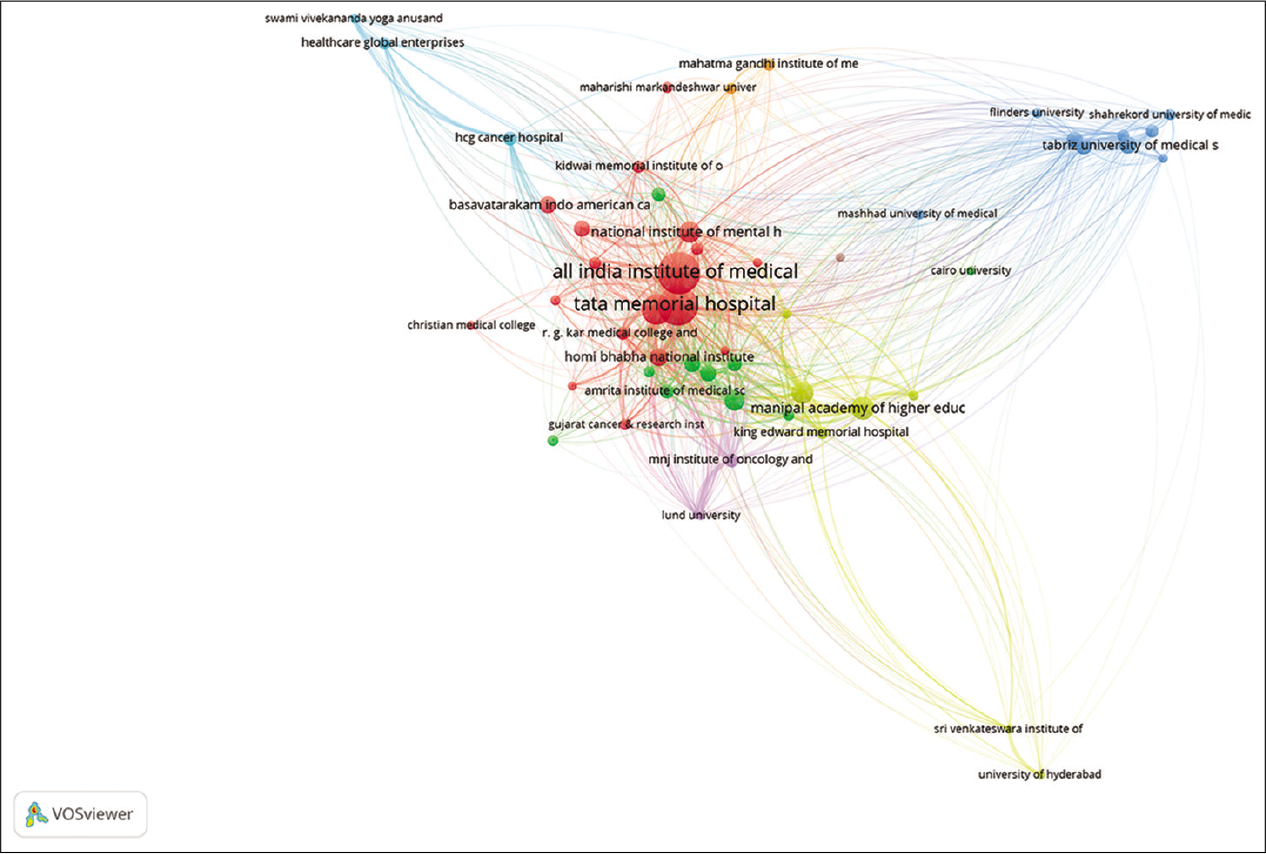
- Bibliometric coupling; organisations (Affiliations).
The threshold was set to a minimum of five documents per organisation. Out of 484 organisations, 53 met the threshold. A strong network could be seen between AIIMS, Tata memorial hospital and NIMHANS.
[Figure 21] represents bibliographic coupling, the unit of analysis being countries. The threshold was set to at least four documents produced by a country. Out of 50 countries, 25 met the threshold. India is one of the central nodes in the network map.

- Bibliographic coupling: Countries.
Cooccurrence map based on text data
[Figure 22] represents the analysis of the titles of studies published in the IJPC; here, a cooccurrence network map was created using the text data extracted from the ‘Titles.’ The binary counting method was chosen for the analysis and the minimum number of occurrences of the term was set to be 5. A total of 132 terms matched the criteria.

- Cooccurrence map of text (Title).
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The bibliometric analysis of IJPC provides a comprehensive bibliometric overview and visualisation of the bibliometric data of the journal. Keeping in mind, the four-step procedure of conducting bibliometric analysis as proposed by Donthu et al.,[8] the analysis was conducted. The purpose of the study is to create a detailed and multifaceted picture of the characteristics of the IJPC to get an insight into the research activity in the field of palliative care in India. Dimensions database was used to mine the bibliographic data where a total of 1046 records from the year 2005 to 2022 (Accessed on January 19, 2022) were downloaded in CSV format. Two software; Biblioshiny by Bibliometrix and VOSviewer were selected for data analysis. The results gave an insight into the growth of the journal over the years. In the beginning years, the number of publications by the journal had somewhat been modest; however, a gradual positive upward trend could be noticed.
Analysis of institutions and countries depicted that mostly the Indian institutions and authors are the leading publishers, followed by Iran and U.K. A strong connection of the IJPC could be seen with leading journals publishing in the field of palliative care globally.
A multiphasic thematic analysis gave us a detailed overview of research themes and research trends over time. To understand the key areas of research and major themes, the bibliometric data were divided into three phases based on the year of publication. Phase I covered the publications from the year 2005 to 2010, Phase II covered the publications from the year 2011 to 2016 and Phase III covered the publications from the year 2017 to 2022 (till January 2022). Phase III was further divided into three more time slices assuming that this phase saw the rise of COVID-19-related research, we further divided this phase into three phases so to isolate the COVID-19-related studies from the rest of the research themes to get a clearer picture of the research themes preCOVID, during COVID and post-COVID period. Time slice 1 covered the data from 2017 to 2019 (the Pre-COVID phase), and Time slice 2 covered the data for 2020. (The emergence of COVID-19) and Time slice 3 covered the data from 2021 to 2022 (Post-COVID phase). The thematic analysis highlighted that cancer, cancer pain, communication, endof-life care and breaking the bad news had been consistent themes during the three phases. Research themes related to psychological, psychosocial and mental health-related aspects of palliative care. Research in paediatric palliative care, head-and-neck cancer, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and breast cancer is a steady rise from the second phase onward. The third phase that saw the emergence of COVID-19 had a rise in pandemic-related research such as psychological effects of COVID, home-based palliative care, telemedicine and community support.
This study would provide the potential authors and general readers of the journal a detailed overview of the most relevant documents and authors to look for in the journal, along with a detailed overview of major, emerging and niche research themes in the field of palliative care in India. It would also encourage new authors and organisations to publish with IJPC for a significant impact.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Available from: https://www.jpalliativecare.com/about-us [Last accessed on 2022 Jan 20]
- Research constituents, intellectual structure, and collaboration patterns in Journal of International Marketing: An analytical retrospective. J Int Market. 2021;29:1-25.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- 2006. Journal citation identity and journal citation image: A portrait of the Journal of Documentation. J Document. 2006;62:30-57.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bibliometric studies on single journals: A review. Malaysian J Lib Inform Sci. 2009;14:17-55.
- [Google Scholar]
- How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133:285-96.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Inform. 2017;11:959-75.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84:523-38.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palliative care in India: Current progress and future needs. Indian J Palliat Care. 2012;18:149.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Communication with relatives and collusion in palliative care: A cross-cultural perspective. Indian J Palliat Care. 2009;15:2.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- "BREAKS" protocol for breaking bad news. Indian J Palliat Care. 2010;16:61.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quality of life outcomes in patients living with stoma. Indian J Palliat Care. 2012;18:176.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effective factors in providing holistic care: A qualitative study. Indian J Palliat Care. 2015;21:214.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quality of life among cancer patients. Indian J Palliat Care. 2017;23:445.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utilization of brief pain inventory as an assessment tool for pain in patients with cancer: A focused review. Indian J Palliat Care. 2011;17:108.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A comparative study on resilience, perceived social support and hopelessness among cancer patients treated with curative and palliative care. Indian J Palliat Care. 2016;22:135.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiritual needs of cancer patients: A qualitative study. Indian J Palliat Care. 2015;21:61.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Physical therapy in palliative care: From symptom control to quality of life: A critical review. Indian J Palliat Care. 2010;16:138.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caring for dying patients: Attitude of nursing students and effects of education. Indian J Palliat Care. 2015;21:192.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factors influencing communication between the patients with cancer and their nurses in oncology wards. Indian J Palliat Care. 2014;20:12.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurses' workplace stressors and coping strategies. Indian J Palliat Care. 2008;14:38.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nurses' perceptions of spirituality and spiritual care giving: A comparison study among all health care sectors in Jordan. Indian J Palliat Care. 2016;22:42.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Complementary and alternative medicine in cancer pain management: A systematic review. Indian J Palliat Care. 2015;21:105.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adverse psychosocial consequences: Compassion fatigue, burnout and vicarious traumatization: Are nurses who provide palliative and hematological cancer care vulnerable? Indian J Palliative Care. 2008;14:23.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Neighborhood network in palliative care. Indian J Palliat Care. 2005;11:6.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Radiation induced oral mucositis. Indian J Palliat Care. 2009;15:95.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depression and demoralization as distinct syndromes: Preliminary data from a cohort of advanced cancer patients. Indian J Palliat Care. 2006;12:8.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Study of nurses' knowledge about palliative care: A quantitative cross-sectional survey. Indian J Palliat Care. 2012;18:122-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J Am Soc Inform Sci. 1973;24:265-9.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Co-authorship networks: An introduction. Complex Networks in Software, Knowledge, and Social Systems In: Intelligent Systems Reference Library. Vol 148. Cham: Springer; 2019.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







