Translate this page into:
Effects of Exercise Training during Concomitant Chemoradiation Therapy in Head-and-Neck Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review
Address for correspondence: Dr. Stephen Rajan Samuel, Department of Physiotherapy, Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Karnataka, India. E-mail: stephen.samuel@manipal.edu
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Existing literature suggests that cancer survivors present with high rates of morbidity due to various treatment and disease-induced factors. Research has shown exercise to be beneficial in improving treatment outcomes and quality of life (QOL). This review was done to collect the current state of exercise-based interventions for cancer survivors in India. From the summarized data, exercise interventions were categorized into resistance training, aerobic training, and home-based walking program in head-and-neck cancers. A broad range of outcomes showed improvement in muscle strength, functional capacity, and QOL and hence supported the benefits of exercise-based interventions in this population. All the data retrieved, therefore, conclude that exercise-based interventions are safe, feasible, and beneficial in patients with head and neck cancer receiving chemoradiation therapy.
Keywords
Aerobic training
exercise interventions
head-and-neck cancer
quality of life
resistance training
INTRODUCTION
Head-and-neck carcinoma is a heterogeneous disease, encompassing a variety of tumors that originate in the hypopharynx, oropharynx, lip, oral cavity, nasopharynx, or larynx. It is considered as the sixth most common cancer worldwide.[1] Head-and-neck cancer is predominantly seen in 25%–30% of the Indian population, whereas 60%–80% presenting with the advanced stage of the disease.[2]
Treatment of head and neck cancer depends on the extensiveness or the stage of the tumor. In the early stages (Stage I and II), surgery has always been the treatment of choice, whereas in the advanced stages of the disease (III and IV, IVa, IVb, and IVc), multimodality treatment (surgery with radiotherapy [RT] and/or chemotherapy, chemoradiation therapy [CRT]) is used.[3]
CRT along with its benefits also results in substantial number of treatment-related adverse effects.[1] Primarily, due to the anatomic location of the tumor, CRT affects the speech, swallowing, and respiratory functions.[4] Adverse effects also extending to fatigue, generalized peripheral muscle weakness that includes muscle wasting, cachexia, and disuse muscle atrophy; and depression often lead to physical inactivity in these patients.[56]
Hence, all of these above factors impair the quality of life (QOL) and daily functional capacity in head and neck cancer patients, facilitating the need for an exercise rehabilitation program.[5] Exercise being an acute intervention shows many effects on the cardiovascular system and lean body mass (LBM) and also reduces the risk of metabolic disorders, when incorporated as an adjunct with chemoradiotherapy.[7] Hence, physical activity in the form of exercise is a possible and effective treatment that may positively impact head and neck cancer patients' body composition, physical functioning capacity, and overall QOL.[8] Thus, this review aims to investigate the current state of exercise-based research in this population.
METHODS/SEARCH STRATEGY
An all-encompassing search was conducted in CINAHL, Cochrane Library, EBSCO, and PubMed Central using keywords – Neoplasms, Head and Neck, Head, Neck Neoplasms, Cancer of Head and Neck, Head and Neck Cancer, Upper Aerodigestive Tract Neoplasms, Training, Resistance, Strength Training, Training, Strength, Strengthening program, Aerobic Exercises, and Aerobic training. Keywords were identified using Medical Subject Heading, synonyms of the words in the title, and keywords from the articles. Boolean operator “AND” and reference list of articles found were used to search articles for the review. Studies that evaluated exercise interventions in head and neck cancer patients on concomitant CRT and the studies published in English-language journals were included for the review. Any of the studies that evaluated cancer survivors admitted to an intensive care unit and yoga intervention were excluded. Furthermore, any studies that included interventions addressing complications such as amputations and nervous system impairment following cancer were excluded. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included in our review. The protocol for the review was constructed by SRS and MD. Two investigators (MD and SRS) independently conducted data search in the above mentioned search engines, and the search results from all the databases were screened independently for eligibility by the two investigators.
All the retrieved data used in this systematic review underwent a qualitative methodological rating given by authors MD and SRS using the PEDro scale. Any differences in the opinion were resolved by discussions between MD and SRS. A data extraction sheet was made to cover all the data regarding the objectives of the study, type of exercise intervention, primary and secondary outcome measures, study design, sample size, participant selection, details of exercise intervention, and adverse events as reported by the study. Data were briefed to highlight the study characteristics, methodological rating score, type of exercise interventions, and outcomes reported from each study.
RESULTS
The following PRISMA flow diagram shown in Figure 1 summarizes the, identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion of the clinical trials. All the retrieved trials that were eligible for the systematic review underwent a quality rating following which a methodological rating was given to each using the PEDro scale [Table 1] for RCTs. The scores ranged from 6 to 10 out of 11, and therefore, the trials were categorized as high quality (6–10). All the studies were reasonably reliable to assess the effect of the intervention on their principle outcome measures.
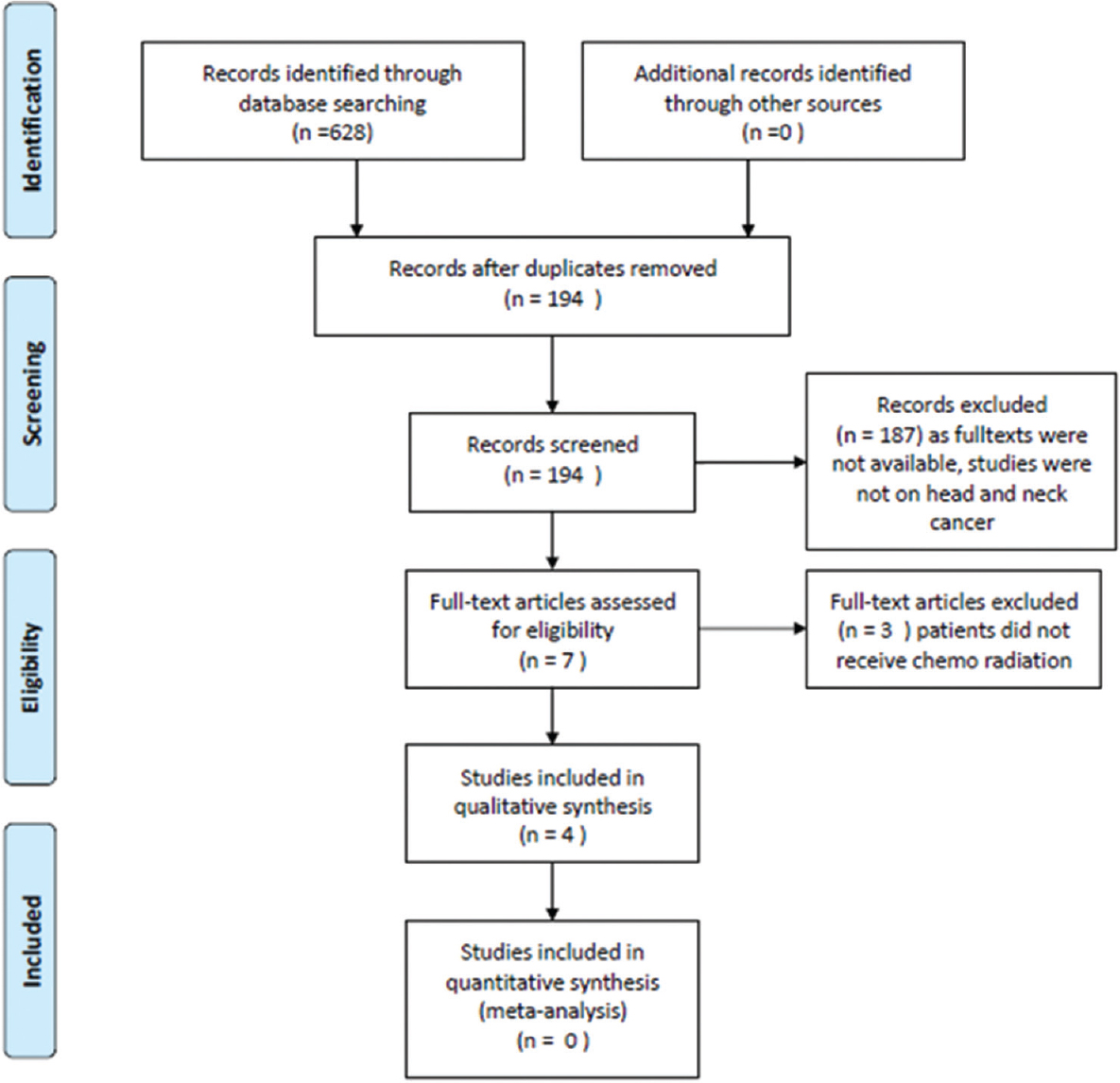
- PRISMA flow diagram
| References | Intervention | Results | PEDro score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Samuel et al. (2013) | First component: Brisk walking program for 15-20 min at an RPE between 3 and 5/10 for 5 days a week for 6 weeks Second component: Active exercise program for both upper and lower limbs 5 days a week for 6 weeks Progression: Active-resisted exercises for biceps, triceps, hamstrings, and quadriceps 8-10 times for 2-3 sets |
Functional capacity evaluated by 6MWT showed significant improvement in the experimental group that underwent the exercise training (P<0.05) QOL also improved with exercise training as well as the PCS was maintained as much as the baseline with no significant deterioration |
9 |
| Zhao, MD et al. (2016) | Resistance program - chest press in squat, wall push up, military press, side arm raises, biceps curl, shoulder shrugs, and calf raises. Weights included dumbbells and inserts into an ankle strap Intensity: 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions of each functional resistance for 7 weeks with rest periods of 2 min Walking program: Five times for 6 min to achieve 30 min of walking each day for 7 weeks |
The MPACT participants had achieved improvement in several strength, mobility, physical activity, diet, and QOL endpoints These trends were statistically significant (P<0.05) in knee strength, mental health, head-and-neck QOL, and barriers to exercise |
6 |
| Samuel et al. (2019) | Control group - three 10-min walk every 5 days a week Experimental group - aerobic exercise (brisk walking 15-20 min) and active resistance exercise: Biceps curl, triceps extension, overhead shoulder flexion, hip flexion and abduction, and quadriceps (knee extension) Intensity: RPE of 3-5/10 for 15-20 min Frequency: 5 days/week |
A 11-week training program showed significant improvement in the functional capacity (P<0.001), QOL (P<0.001), and prevention of worsening of fatigue (P<0.001) in the exercise group | 8 |
| Lonkvist et al. (2017) | Resistance training: Large muscle groups Intensity and volume progression: From 2 to 3 sets with a load corresponding to 15-8 RM Frequency: 36 training sessions, i.e., thrice weekly for 12 weeks Control group: No restriction on any physical activity but no organized training |
12-week resistance training showed significant improvement in muscle strength, muscle mass, body composition, and QOL. This study also proved to be safe and feasible in terms of resistance training | 8 |
6MWT: 6-min walk test, PCS: Physical component score, QOL: Quality of life, RPE: Rating of perceived exertion, RM: Repetition maximum
All the studies characterized in this review were RCTs. Three types of exercise interventions were noted: strength training, aerobic training, and home-based walking program. All details regarding the study design, sample size, cancer management, and type of exercise intervention and outcome measures assessed are summarized in Table 2, and detailed explanation of exercise intervention and their respective results are mentioned in Table 1.
| References | Study design | Sample size (n) | Cancer management | Exercise intervention | Outcomes assessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samuel et al. (2013) | RCT | 48 | CRT | Aerobic and strength training | Functional capacity and QOL |
| Zhao MD et al. (2016) | PCT | 11 | CRT | Functional resistance program and walking program | Muscle strength, functional mobility, and self-reported QOL |
| Samuel et al. (2019) | RCT | 148 | CRT | Aerobic walking and active resistance training program | Functional capacity and QOL |
| Lonkvist et al. (2017) | RCT | 72 | CRT | Progressive resistance training | LBM, body composition, muscle strength, functional performance, self-reported physical activity, and QOL |
RCT: Randomized control trial, CRT: Chemoradiation therapy, QOL: Quality of life, LBM: Lean body mass, PCT: Pilot controlled trial
DISCUSSION
The present study is the first comprehensive systematic review on exercise interventions for head and neck cancer survivors from India. Cancer survivors are known to be at an increased risk of developing chronic diseases and are more likely to die from non-cancer causes. Indians are considered to have a lower threshold for developing chronic diseases, and therefore, India currently has a high burden of chronic diseases. Hence, this could be a potential area for research. Physiotherapy-based interventions have been shown to reduce the recurrence of cancer, anxiety, depression, pain, and body mass index and improve survival, cardiorespiratory fitness, strength, fatigue, range of motion, appetite, and QOL.[9] The present review showed three different types of exercise protocol and intervention to note its effect on strength, aerobic functional capacity, and QOL in head and neck cancer patients undergoing CRT. Exercise for this review is operationally defined as exercise intervention in the form of aerobic and resistance training administered to head and neck cancer survivors on concomitant chemoradiotherapy. A study conducted by Samuel et al. in 2013 evaluated the effect of exercise training on the functional capacity and QOL in head and neck cancer patients. In this study, the author justified that low functional capacity in these patients due to the harmful concomitant side effects of CRT could be counteracted by a structured exercise training program. Thus, the study showed positive results and improvement in the functional capacity through exercise training evaluated by 6-min walk distance and Short Form-36 (SF-36) questionnaires. The authors hypothesized that exercise positively influences the oxygen transport thus increasing the oxygen uptake by the tissues and prevents the peripheral muscle fatigue, thereby restoring the energy, improving strength, and maintaining cardiorespiratory endurance.[10] Another study conducted by Zhao et al. aimed at studying the impact of resistance training and walking program on different components in head and neck cancer patients. These components involved strength, mobility, physical activity, diet, and QOL that were assessed using dynamometers, self-reported physical activity questionnaires, 6-min walk tests, BMI, SF-36 questionnaire, respectively. This study showed gradual changes and improvement in the above outcomes from 7th to 14th weeks of the study. One of the important study limitations was a small sample size which limited the statistical power, but the assessment and intervention showed feasible results.[11] A similar randomized trial study by Lonkvist et al. in 2017 was conducted to evaluate the changes and effect of progressive resistance training (PRT) in LBM, physical function, and mobility after 12 weeks of training. These were evaluated using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, muscle biopsies to evaluate the muscle fiber change. A twelve-week period was chosen as it was considered a sufficient period of PRT to affect LBM. Although this study found that PRT is feasible and safe during CRT for head and neck cancer, it pointed the need for a randomized trial to reveal the potential effect of PRT during CRT in HNC.[12] In 2019, Samuel et al. published an RCT to evaluate the effect of exercise training on strength, functional capacity, and QOL. Results showed beneficial improvements in the above outcomes and that aerobic and resistance training are both safe and feasible during chemoradiation for head and neck cancer.[13] The studies retrieved by this review help us to understand that exercise is feasible during the course of CRT in patients with head and neck cancer. To summarize, the following outcome measures, i.e., muscle strength, mobility, functional capacity, and QOL, have been studied and the following exercise interventions in the domain of aerobic and resistance training have been studied.
We further suggest that future studies should use the above outcomes and following types of training such as interval training can be studied in the domain of aerobic, e.g., brisk walking, deep breathing exercises, cycling, and resistance training involving theraband exercises, and weights for major muscle groups such as the biceps, triceps, pectorals, hip abductors, extensors, quadriceps, and gastrocnemius muscles. We also recommend more studies in this area to strengthen the current body of evidence in this field of exercise oncology.
CONCLUSION
All these data, therefore, conclude that exercise-based intervention is safe, feasible, and beneficial in patients with head and neck cancer receiving CRT.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- Head and neck cancer: Improving outcomes with a multidisciplinary approach. Cancer Manag Res. 2017;9:363-71.
- [Google Scholar]
- Management of head and neck cancer: Surgical and nonsurgical. Otorhinolaryngol Clin Int J. 2010;2:77-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Complications of head and neck cancer surgery – Prevention and management. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:433-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Quality of life of patients with head and neck cancer. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79:82-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Factors affecting muscle strength in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. J Nov Physiother Rehabil. 2017;1:56-66.
- [Google Scholar]
- Impact of resistance training in cancer survivors: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45:2080-90.
- [Google Scholar]
- The impact of physical activity on health-related fitness and quality of life for patients with head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50:325-38.
- [Google Scholar]
- Exercise-based interventions for cancer survivors in India: A systematic review. Springerplus. 2015;4:655.
- [Google Scholar]
- Effect of exercise training on functional capacity quality of life in head neck cancer patients receiving chemoradiotherapy. Indian J Med Res. 2013;137:515-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Maintaining physical activity during head and neck cancer treatment: Results of a pilot controlled trial. Head Neck. 2016;38(Suppl 1):E1086-96.
- [Google Scholar]
- Progressive resistance training in head and neck cancer patients during concomitant chemoradiotherapy – Design of the DAHANCA 31 randomized trial. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:400.
- [Google Scholar]
- Effectiveness of exercise-based rehabilitation on functional capacity and quality of life in head and neck cancer patients receiving chemo-radiotherapy. Support Care Cancer. 2019;27:3913-20.
- [Google Scholar]






